Parkinsonism in Genetic Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36699000
- PMCID: PMC9847320
- DOI: 10.1002/mdc3.13577
Parkinsonism in Genetic Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: With advances in clinical genetic testing, associations between genetic neurodevelopmental disorders and parkinsonism are increasingly recognized. In this review, we aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of reports on parkinsonism in genetic neurodevelopmental disorders and summarize findings related to genetic diagnosis, clinical features and proposed disease mechanisms.
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted in PubMed and Embase on June 15, 2021. Search terms for parkinsonism and genetic neurodevelopmental disorders, using generic terms and the Human Phenotype Ontology, were combined. Study characteristics and descriptive data were extracted from the articles using a modified version of the Cochrane Consumers and Communication Review Group's data extraction template. The protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42020191035).
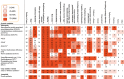
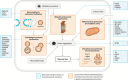
Results: The literature search yielded 208 reports for data-extraction, describing 69 genetic disorders in 422 patients. The five most reported from most to least frequent were: 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, beta-propeller protein-associated neurodegeneration, Down syndrome, cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, and Rett syndrome. Notable findings were an almost equal male to female ratio, an early median age of motor onset (26 years old) and rigidity being more common than rest tremor. Results of dopaminergic imaging and response to antiparkinsonian medication often supported the neurodegenerative nature of parkinsonism. Moreover, neuropathology results showed neuronal loss in the majority of cases. Proposed disease mechanisms included aberrant mitochondrial function and disruptions in neurotransmitter metabolism, endosomal trafficking, and the autophagic-lysosomal and ubiquitin-proteasome system.
Conclusion: Parkinsonism has been reported in many GNDs. Findings from this study may provide clues for further research and improve management of patients with GNDs and/or parkinsonism.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; genetic; intellectual disability; neurodevelopmental disorder; parkinsonism.
© 2022 The Authors. Movement Disorders Clinical Practice published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported financially by Stichting Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek's Heeren Loo (2210100). The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study, preparation of the review, or approval of the manuscript. The authors report no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dementia in Rare Genetic Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Systematic Literature Review.Neurology. 2024 Jun 11;102(11):e209413. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209413. Epub 2024 May 17. Neurology. 2024. PMID: 38759134 Free PMC article.
-
Chapter 33: the history of movement disorders.Handb Clin Neurol. 2010;95:501-46. doi: 10.1016/S0072-9752(08)02133-7. Handb Clin Neurol. 2010. PMID: 19892136 Review.
-
Parkinsonism in children: Clinical classification and etiological spectrum.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021 Jan;82:150-157. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 33109474 Review.
-
Clinical and neuroimaging phenotypes of genetic parkinsonism from infancy to adolescence.Brain. 2020 Mar 1;143(3):751-770. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz345. Brain. 2020. PMID: 31800013 Review.
-
Identification of parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease.Drugs Today (Barc). 2002 Oct;38(10):677-86. doi: 10.1358/dot.2002.38.10.740195. Drugs Today (Barc). 2002. PMID: 12582453 Review.
Cited by
-
Do we care? Reporting of genetic diagnoses in multidisciplinary intellectual disability care: a retrospective chart review.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Sep 16;19(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03323-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 39285396 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine synthesis and transport: current and novel therapeutics for parkinsonisms.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Jun 26;52(3):1275-1291. doi: 10.1042/BST20231061. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38813865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dementia in Rare Genetic Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Systematic Literature Review.Neurology. 2024 Jun 11;102(11):e209413. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209413. Epub 2024 May 17. Neurology. 2024. PMID: 38759134 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Pathobiology of GM1 Gangliosidosis from Single-Nucleus Transcriptomic Analysis of CNS Cells in a Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 8;25(17):9712. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179712. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273659 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the Phenotypic Spectrum and Complexity of Movement Disorders in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome.Eur J Neurol. 2025 Jun;32(6):e70256. doi: 10.1111/ene.70256. Eur J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40530538 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

