Ameliorative effect of taurine against diabetes and renal-associated disorders (Review)
- PMID: 36699147
- PMCID: PMC9855276
- DOI: 10.3892/mi.2021.3
Ameliorative effect of taurine against diabetes and renal-associated disorders (Review)
Abstract
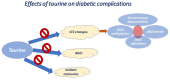
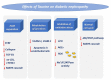
To develop novel therapeutic methods for both diabetic and renal disorders, scientists had initially focused on elucidating the molecular mechanisms of taurine in established cell lines and mouse models. Although a large amount of data have been revealed, taurine has been confirmed to be the next step of novel promising therapeutic interventions against diabetic disorders. Taurine appears to ameliorate diabetes 1-related complications in various organs through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-hormonal actions. In type 2 diabetes, taurine has been positively implicated in glucose homeostasis, exerting potent hypoglycemic, anti-obesity, hypotensive and hypolipidemic effects. Of particular interest is that taurine provides protection against renal dysfunction, including hypertension and proteinuria, specific glomerular and tubular disorders, acute and chronic renal conditions, and diabetic nephropathy. The ameliorative effects of taurine against renal disorders are based on its osmoregulatory properties, its association with signaling pathways and its association with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Further clinical studies are required to ensure the importance of research findings.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic nephropathy; renal transplantation; taurine.
Copyright: © Baliou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DAS is the Editor in Chief for the journal, but had no personal involvement in the reviewing process, or any influence in terms of adjudicating on the final decision, for this article. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Chaudhury A, Duvoor C, Reddy Dendi VS, Kraleti S, Chada A, Ravilla R, Marco A, Shekhawat NS, Montales MT, Kuriakose K, et al. Clinical review of antidiabetic drugs: implications for type 2 diabetes mellitus management. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2017;8(6) doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
