Robot-assisted cannulated compression screw internal fixation for treatment of femoral neck fracture in children: A case series of ten patients
- PMID: 36699299
- PMCID: PMC9869125
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.1105717
Robot-assisted cannulated compression screw internal fixation for treatment of femoral neck fracture in children: A case series of ten patients
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the safety and efficacy of robot-assisted cannulated compression screw internal fixation in the treatment of femoral neck fracture in children.
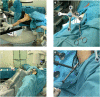
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the data of ten children with femoral neck fractures treated by robot-assisted internal fixation from January 2020 to June 2021. The clinical and radiological characteristics, operation duration, and fluoroscopy frequency of robot-assisted screws placement together with the complications and function were evaluated. At the 12-month follow-up, the hip joint function was evaluated using the Ratliff classification.
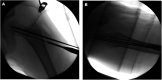
Results: Ten children, six boys and four girls, aged 4-14 years were included. There were eight type II and three type III femoral neck fractures using the Delbet classification. In the process of robot-assisted internal fixation, the median of fluoroscopy frequency was 22 times and the median of operation duration was 47 min. The median of screw parallelism was 1.33° and 0.66° on the anteroposterior and lateral x-ray films, and the median of screw distribution was 41.86% and 44.93% on the anteroposterior and lateral x-ray films, respectively. At the 12-month follow-up, there were two cases of femoral head necrosis, and fracture healing was achieved in all patients, of which eight fractures were excellent and three were good by the Ratliff function classification.
Discussion: The application of robot-assisted cannulated compression screw internal fixation could help us achieve more safe and accurate screw placement, as well as a good treatment effect for children's femoral neck fractures.
Level of evidence: Level IV. retrospective case series.
Keywords: children; femoral neck fracture; internal fixation; robot-assisted; screw.
© 2023 Feng, Yao, Liu, Guo, Zhu, Song, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures with Cannulated Screw Invasive Internal Fixation Assisted by Orthopaedic Surgery Robot Positioning System.Orthop Surg. 2019 Oct;11(5):864-872. doi: 10.1111/os.12548. Orthop Surg. 2019. PMID: 31663277 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of curative effect between Tianji robot assisted screw placement and traditional cannulated screw internal fixation for femoral neck fracture].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023 Mar 25;36(3):221-5. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2023.03.005. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023. PMID: 36946012 Chinese.
-
Robot-assisted Percutaneous Cannulated Screw Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures: Preliminary Clinical Results.Orthop Surg. 2019 Feb;11(1):34-41. doi: 10.1111/os.12430. Orthop Surg. 2019. PMID: 30834705 Free PMC article.
-
[Lateral approach to pediatric femoral neck fractures].Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2021 Feb;33(1):15-22. doi: 10.1007/s00064-020-00693-5. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2021. PMID: 33404664 Review. German.
-
Medial femoral plate with cannulated screw for Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture: A meta-analysis.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021;34(2):169-177. doi: 10.3233/BMR-200183. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33164925 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term outcome of robotic-guided closed reduction internal fixation for Delbet II femoral neck fractures in children.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Sep 6;19(1):543. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05035-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39237987 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

