ExplorePipolin: reconstruction and annotation of piPolB-encoding bacterial mobile elements from draft genomes
- PMID: 36699382
- PMCID: PMC9710591
- DOI: 10.1093/bioadv/vbac056
ExplorePipolin: reconstruction and annotation of piPolB-encoding bacterial mobile elements from draft genomes
Abstract
Motivation: Detailed and accurate analysis of mobile genetic elements (MGEs) in bacteria is essential to deal with the current threat of multiresistant microbes. The overwhelming use of draft, contig-based genomes hinder the delineation of the genetic structure of these plastic and variable genomic stretches, as in the case of pipolins, a superfamily of MGEs that spans diverse integrative and plasmidic elements, characterized by the presence of a primer-independent DNA polymerase.
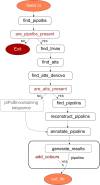
Results: ExplorePipolin is a Python-based pipeline that screens for the presence of the element and performs its reconstruction and annotation. The pipeline can be used on virtually any genome from diverse organisms and of diverse quality, obtaining the highest-scored possible structure and reconstructed out of different contigs if necessary. Then, predicted pipolin boundaries and pipolin encoded genes are subsequently annotated using a custom database, returning the standard file formats suitable for comparative genomics of this mobile element.
Availability and implementation: All code is available and can be accessed here: github.com/pipolinlab/ExplorePipolin.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics Advances online.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pipolins are bimodular platforms that maintain a reservoir of defense systems exchangeable with various bacterial genetic mobile elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Nov 11;52(20):12498-12516. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae891. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39404074 Free PMC article.
-
High diversity and variability of pipolins among a wide range of pathogenic Escherichia coli strains.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 27;10(1):12452. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69356-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32719405 Free PMC article.
-
Beav: a bacterial genome and mobile element annotation pipeline.mSphere. 2024 Aug 28;9(8):e0020924. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00209-24. Epub 2024 Jul 22. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39037262 Free PMC article.
-
ISEScan: automated identification of insertion sequence elements in prokaryotic genomes.Bioinformatics. 2017 Nov 1;33(21):3340-3347. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx433. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 29077810
-
mobileOG-db: a Manually Curated Database of Protein Families Mediating the Life Cycle of Bacterial Mobile Genetic Elements.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Sep 22;88(18):e0099122. doi: 10.1128/aem.00991-22. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36036594 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pipolins are bimodular platforms that maintain a reservoir of defense systems exchangeable with various bacterial genetic mobile elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Nov 11;52(20):12498-12516. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae891. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39404074 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

