Comparative transcriptomic analyzes of human lung epithelial cells infected with wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and its variant with a 12-bp missing in the E gene
- PMID: 36699595
- PMCID: PMC9868179
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1079764
Comparative transcriptomic analyzes of human lung epithelial cells infected with wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and its variant with a 12-bp missing in the E gene
Abstract
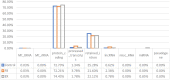
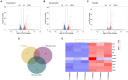
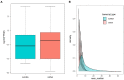
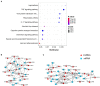
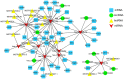
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel coronavirus that caused a global outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. To elucidate the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 replication and immunogenicity, we performed a comparative transcriptome profile of mRNA and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in human lung epithelial cells infected with the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type strain (8X) and the variant with a 12-bp deletion in the E gene (F8). In total, 3,966 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and 110 differentially expressed lncRNA (DE-lncRNA) candidates were identified. Of these, 94 DEGs and 32 DE-lncRNAs were found between samples infected with F8 and 8X. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyzes revealed that pathways such as the TNF signaling pathway and viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor were involved. Furthermore, we constructed a lncRNA-protein-coding gene co-expression interaction network. The KEGG analysis of the co-expressed genes showed that these differentially expressed lncRNAs were enriched in pathways related to the immune response, which might explain the different replication and immunogenicity properties of the 8X and F8 strains. These results provide a useful resource for studying the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Keywords: COVID-19; E gene; RNA-seq; immune response; lncRNAs.
Copyright © 2023 Sun, Sun, Zhu, Li, Xu, Lu, Tang, Wu, Li, Yao and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Genomic Characterization Analysis of lncRNAs in Cells With Porcine Delta Coronavirus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 28;10:3036. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03036. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32063887 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Coding and Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) Transcriptional Landscape in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Bronchial Epithelial Cells Highlight a Role for Interferon and Inflammatory Response.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 7;11(7):760. doi: 10.3390/genes11070760. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32646047 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals immunoregulation mechanism of lncRNA-mRNA in gill and skin of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in response to Cryptocaryon irritans infection.BMC Genomics. 2022 Mar 15;23(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08431-w. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35287569 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of lncRNAs and miRNAs in SARS-CoV-2 infection.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jul 27;11:1229393. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1229393. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37576600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current understanding on long non-coding RNAs in immune response to COVID-19.Virus Res. 2023 Jan 2;323:198956. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2022.198956. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 36208691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differentially expressed ncRNAs as key regulators in infection of human bronchial epithelial cells by the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 May 14;36(2):102559. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102559. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40510596 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Profiling of SARS-CoV-2-Infected Calu-3 Cells Reveals Immune-Related Signaling Pathways.Pathogens. 2023 Nov 20;12(11):1373. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111373. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003837 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary deletions within the SARS-CoV-2 genome as signature trends for virus fitness and adaptation.J Virol. 2024 Jan 23;98(1):e0140423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01404-23. Epub 2023 Dec 13. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38088350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Babraham Bioinformatics . (2022). FastQC. Available at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (Accessed July 20, 2022).
-
- Castano-Rodriguez C., Honrubia J. M., Gutierrez-Alvarez J., DeDiego M. L., Nieto-Torres J. L., Jimenez-Guardeno J. M., et al. . (2018). Role of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus Viroporins E, 3a, and 8a in replication and pathogenesis. MBio 9, e02325–e02317. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02325-17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

