Impact of KvLQT1 potassium channel modulation on alveolar fluid homeostasis in an animal model of thiourea-induced lung edema
- PMID: 36699692
- PMCID: PMC9868633
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1069466
Impact of KvLQT1 potassium channel modulation on alveolar fluid homeostasis in an animal model of thiourea-induced lung edema
Abstract
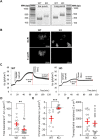
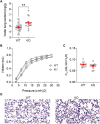
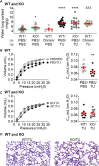
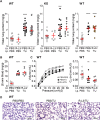
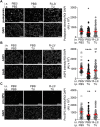
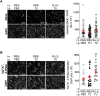
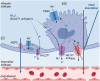
Alveolar ion and fluid absorption is essential for lung homeostasis in healthy conditions as well as for the resorption of lung edema, a key feature of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Liquid absorption is driven by active transepithelial sodium transport, through apical ENaC Na+ channels and basolateral Na+/K+-ATPase. Our previous work unveiled that KvLQT1 K+ channels also participate in the control of Na+/liquid absorption in alveolar epithelial cells. Our aim was to further investigate the function of KvLQT1 channels and their interplay with other channels/transporters involved in ion/liquid transport in vivo using adult wild-type (WT) and KvLQT1 knock-out (KO) mice under physiological conditions and after thiourea-induced lung edema. A slight but significant increase in water lung content (WLC) was observed in naïve KvLQT1-KO mice, relative to WT littermates, whereas lung function was generally preserved and histological structure unaltered. Following thiourea-induced lung edema, KvLQT1-KO did not worsen WLC or lung function. Similarly, lung edema was not aggravated by the administration of a KvLQT1 inhibitor (chromanol). However, KvLQT1 activation (R-L3) significantly reduced WLC in thiourea-challenged WT mice. The benefits of R-L3 were prevented in KO or chromanol-treated WT mice. Furthermore, R-L3 treatment had no effect on thiourea-induced endothelial barrier alteration but restored or enhanced the levels of epithelial alveolar AQP5, Na+/K+-ATPase, and ENaC expressions. Altogether, the results indicate the benefits of KvLQT1 activation in the resolution of lung edema, probably through the observed up-regulation of epithelial alveolar channels/transporters involved in ion/water transport.
Keywords: AQP5; ENaC; Na+/K+-ATPase; animal model; ion/liquid transport; lung homeostasis; potassium channels; pulmonary edema.
Copyright © 2023 Aubin Vega, Girault, Adam, Chebli, Privé, Maillé, Robichaud and Brochiero.
Conflict of interest statement
AR is employed by SCIREQ Scientific Respiratory Equipment Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Function of KvLQT1 potassium channels in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced acute lung injury.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 20;15:1345488. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1345488. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38444763 Free PMC article.
-
K+ channels regulate ENaC expression via changes in promoter activity and control fluid clearance in alveolar epithelial cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1818(7):1682-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.02.025. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22406554
-
Regulation of ENaC and CFTR expression with K+ channel modulators and effect on fluid absorption across alveolar epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):L1207-19. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00376.2005. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16891388
-
Mechanisms of pulmonary edema clearance during acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: role of the Na,K-ATPase.Crit Care Med. 2003 Apr;31(4 Suppl):S248-52. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000057895.22008.EC. Crit Care Med. 2003. PMID: 12682448 Review.
-
Treatment of pulmonary edema by ENaC activators/stimulators.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;6(1):13-27. doi: 10.2174/1874467211306010003. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23547931 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in a murine model of acute lung injury.Exp Physiol. 2024 Jun;109(6):966-979. doi: 10.1113/EP091682. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Exp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38594909 Free PMC article.
-
Sex and disease regulate major histocompatibility complex class I expression in human lung epithelial cells.Physiol Rep. 2024 Sep;12(17):e70025. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70025. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39223101 Free PMC article.
-
Function of KvLQT1 potassium channels in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced acute lung injury.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 20;15:1345488. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1345488. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38444763 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-Reparative Effects of KvLQT1 Potassium Channel Activation in a Mouse Model of Acute Lung Injury Induced by Bleomycin.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 7;26(15):7632. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157632. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardou O., Privé A., Migneault F., Roy-Camille K., Dagenais A., Berthiaume Y., et al. (2012). K+ channels regulate ENaC expression via changes in promoter activity and control fluid clearance in alveolar epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Biomembr. 1818, 1682–1690. 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.02.025 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

