The Effectiveness of Personalized Nursing on Quality of Life in Cardiovascular Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 36700041
- PMCID: PMC9870693
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/4689732
The Effectiveness of Personalized Nursing on Quality of Life in Cardiovascular Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Aims: This study aimed to examine the potential effectiveness of personalized nursing interventions on improving the heart-related quality of life of patients with CVDs versus an usual care.
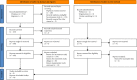
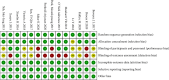
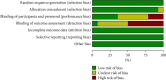
Design: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Data Sources. The study researched the article between January 2011 and December 2021 from four electronic databases: PubMed, Embase, Cochrane library, and Web of Science. Review Methods. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) related to personalized nursing in CVDs population were included. The main variables were analyzed by standardized mean differences with 95% confidence intervals and heterogeneity was used by the I 2 test and P value.
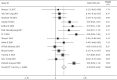
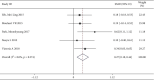
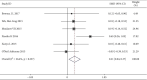
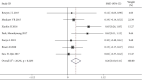
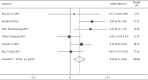
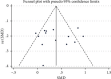
Results: Of 734 studies, fourteen articles were eligible for this study. Personalized nursing significantly improved the quality of life [SMD = 0.39, 95% CI (0.29, 0.49)] with obvious heterogeneity (P = 0.000, I 2 = 66.1%) which needs to be further subgroup analyzed. The nurse-led intervention was considered the main-related effect to influence the heterogeneity with value of 0.39 (I2 = 66.1%, P = 0.000; Group 1: I2 = 48.4%, P = 0.071, and Group 2: I2 = 0.0%,. In addition, related results of athletic ability and mental health and follow-up and education in the intervention had higher level of quality of life compared to the control group [SMD = 0.27, 95% CI (0.10, 0.44); SMD = 0.21, 95% CI (0.04, 0.37); SMD = 0.39, 95% CI (0.29, 0.49) and SMD = 0.28, 95% CI (0.11, 0.44)].
Conclusion: Effectiveness studies of personalized care focus on more relevant outcomes have higher health outcomes, whereas evidence of the effectiveness of personalized nursing approach is still limited. Therefore, more and more high-quality RCT are needed.
Copyright © 2023 Min Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kyriakou M., Middleton N., Ktisti S., Philippou K., Lambrinou E. Supportive care interventions to promote health-related quality of life in patients living with heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Lung & Circulation . 2020;29(11):1633–1647. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2020.04.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kmiecik J., Poli A., Brons N. H., et al. Elevated CD3+ and CD8+ tumor-infiltrating immune cells correlate with prolonged survival in glioblastoma patients despite integrated immunosuppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment and at the systemic level. Journal of Neuroimmunology . 2013;264:71–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.08.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khademian Z., Kazemi Ara F., Gholamzadeh S. The effect of self care education based on orem’s nursing theory on quality of life and self-efficacy in patients with hypertension: a quasi-experimental study. International Journal of Community-Based Nursing and Midwifery . 2020;8(2):140–149. doi: 10.30476/IJCBNM.2020.81690.0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

