Application and trend of bioluminescence imaging in metabolic syndrome research
- PMID: 36700071
- PMCID: PMC9868317
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1113546
Application and trend of bioluminescence imaging in metabolic syndrome research
Abstract
Bioluminescence imaging is a non-invasive technology used to visualize physiological processes in animals and is useful for studying the dynamics of metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a broad spectrum of diseases which are rapidly increasing in prevalence, and is closely associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and circadian rhythm disorder. To better serve metabolic syndrome research, researchers have established a variety of animal models expressing luciferase, while also committing to finding more suitable luciferase promoters and developing more efficient luciferase-luciferin systems. In this review, we systematically summarize the applications of different models for bioluminescence imaging in the study of metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: adipose inflammation; bioluminescence imaging; circadian rhythm disorders; metabolic syndrome; model; non-alcoholic fatty liver; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Wang, Wang, Zhang, Liu, Cheng, Zhu, Zhong, Hu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

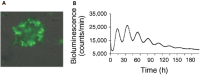
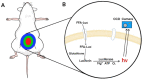
Similar articles
-
Role of the Circadian Clock in the Metabolic Syndrome and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Dec;63(12):3187-3206. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5242-x. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30121811 Review.
-
Uptake kinetics and biodistribution of 14C-D-luciferin--a radiolabeled substrate for the firefly luciferase catalyzed bioluminescence reaction: impact on bioluminescence based reporter gene imaging.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008 Dec;35(12):2275-85. doi: 10.1007/s00259-008-0870-6. Epub 2008 Jul 26. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008. PMID: 18661130 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between pancreas steatosis and the risk of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in Chinese adolescents with concurrent obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Pediatr Obes. 2020 Sep;15(9):e12653. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12653. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Pediatr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32351030 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of d-luciferin for bioluminescence to detect gene expression in freely moving mice for long durations.Luminescence. 2021 Feb;36(1):94-98. doi: 10.1002/bio.3917. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Luminescence. 2021. PMID: 32721066
-
[Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, as a component of the metabolic syndrome, and its causal correlations with other extrahepatic diseases].Orv Hetil. 2017 Dec;158(52):2051-2061. doi: 10.1556/650.2017.30936. Orv Hetil. 2017. PMID: 29285942 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Luminescence Probes in Bio-Applications: From Principle to Practice.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;14(7):333. doi: 10.3390/bios14070333. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

