Study on the molecular mechanism of anti-liver cancer effect of Evodiae fructus by network pharmacology and QSAR model
- PMID: 36700075
- PMCID: PMC9868320
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1060500
Study on the molecular mechanism of anti-liver cancer effect of Evodiae fructus by network pharmacology and QSAR model
Abstract
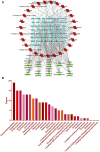
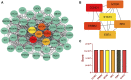
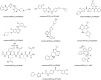
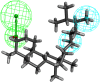
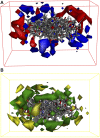
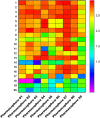
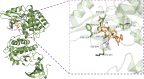
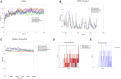
Introduction: Evodiae Fructus (EF) is the dried, near ripe fruit of Euodia rutaecarpa (Juss.) Benth in Rutaceae. Numerous studies have demonstrated its anti-liver cancer properties. However, the molecular mechanism of Evodiae fructus against liver cancer and its structure-activity connection still require clarification. Methods: We utilized network pharmacology and a QSAR (2- and 3-dimensional) model to study the anti-liver cancer effect of Evodiae fructus. First, by using network pharmacology to screen the active substances and targets of Evodiae fructus, we investigated the signaling pathways involved in the anti-liver cancer actions of Evodiae fructus. The 2D-QSAR pharmacophore model was then used to predict the pIC50 values of compounds. The hiphop method was used to create an ideal 3D-QSAR pharmacophore model for the prediction of Evodiae fructus compounds. Finally, molecular docking was used to validate the rationality of the pharmacophore, and molecular dynamics was used to disclose the stability of the compounds by assessing the trajectories in 10 ns using RMSD, RMSF, Rg, and hydrogen bonding metrics. Results: In total, 27 compounds were acquired from the TCMSP and TCM-ID databases, and 45 intersection targets were compiled using Venn diagrams. Network integration analysis was used in this study to identify SRC as a primary target. Key pathways were discovered by KEGG pathway analysis, including PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, and ErbB signaling pathway. Using a 2D-QSAR pharmacophore model and the MLR approach to predict chemical activity, ten highly active compounds were found. Two hydrophobic features and one hydrogen bond acceptor feature in the 3D-QSAR pharmacophore model were validated by training set chemicals. The results of molecular docking revealed that 10 active compounds had better docking scores with SRC and were linked to residues via hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds. Molecular dynamics was used to show the structural stability of obacunone, beta-sitosterol, and sitosterol. Conclusion:Pharmacophore 01 has high selectivity and the ability to distinguish active and inactive compounds, which is the optimal model for this study. Obacunone has the optimal binding ability with SRC. The pharmacophore model proposed in this study provides theoretical support for further screening effective anti-cancer Chinese herbal compounds and optimizing the compound structure.
Keywords: Euodiae fructus; QSAR model; liver cancer; molecular docking; molecular dynamics simulation; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2023 Chen and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Network pharmacology-based screening of the active ingredients and mechanisms of evodiae fructus anti-glioblastoma multiforme.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 30;101(39):e30853. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030853. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36181021 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular authentication and quality control using a high performance liquid chromatography technique of Fructus Evodiae.Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Feb;31(2):312-5. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.312. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008. PMID: 18239294
-
Investigative on the Molecular Mechanism of Licorice Flavonoids Anti-Melanoma by Network Pharmacology, 3D/2D-QSAR, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation.Front Chem. 2022 Mar 2;10:843970. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.843970. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35308797 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatographic and mass spectrometric technologies for chemical analysis of Euodiae fructus: A review.Phytochem Anal. 2023 Jan;34(1):5-29. doi: 10.1002/pca.3187. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Phytochem Anal. 2023. PMID: 36442477 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of hepatotoxicity induced by compounds occurring in Evodiae Fructus.Drug Metab Rev. 2023 Feb-May;55(1-2):75-93. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2023.2180027. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Drug Metab Rev. 2023. PMID: 36803497 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the toxicity-effect relationship and action patterns of traditional Chinese medicines from a smart data perspective: a comprehensive review.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 16;14:1278014. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1278014. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37915415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obacunone, a Promising Phytochemical Triterpenoid: Research Progress on Its Pharmacological Activity and Mechanism.Molecules. 2024 Apr 15;29(8):1791. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081791. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of RNA-sequencing data analysis, network pharmacology, molecular docking techniques to investigate the mechanism of Prunella vulgaris L. in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 12;16(1):726. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02563-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40353950 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a QSAR Model Based on Flavonoids and Screening of Natural Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 7;15(15):3489. doi: 10.3390/nu15153489. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571426 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling potent Glycyrrhiza glabra flavonoids as AKT1 inhibitors using network pharmacology and machine learning-assisted QSAR.Mol Divers. 2025 Aug;29(4):3607-3635. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11210-w. Epub 2025 May 8. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40335842
References
-
- Adelusi T. I., Abdul-Hammed M., Idris M. O., Oyedele Q. K., Adedotun I. O. (2021). Molecular dynamics, quantum mechanics and docking studies of some Keap1 inhibitors - an insight into the atomistic mechanisms of their antioxidant potential. Heliyon 7 (6), e07317. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07317 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

