DLiP-PPI library: An integrated chemical database of small-to-medium-sized molecules targeting protein-protein interactions
- PMID: 36700083
- PMCID: PMC9868583
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1090643
DLiP-PPI library: An integrated chemical database of small-to-medium-sized molecules targeting protein-protein interactions
Abstract
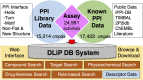
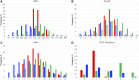
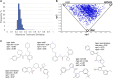
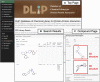
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are recognized as important targets in drug discovery. The characteristics of molecules that inhibit PPIs differ from those of small-molecule compounds. We developed a novel chemical library database system (DLiP) to design PPI inhibitors. A total of 32,647 PPI-related compounds are registered in the DLiP. It contains 15,214 newly synthesized compounds, with molecular weight ranging from 450 to 650, and 17,433 active and inactive compounds registered by extracting and integrating known compound data related to 105 PPI targets from public databases and published literature. Our analysis revealed that the compounds in this database contain unique chemical structures and have physicochemical properties suitable for binding to the protein-protein interface. In addition, advanced functions have been integrated with the web interface, which allows users to search for potential PPI inhibitor compounds based on types of protein-protein interfaces, filter results by drug-likeness indicators important for PPI targeting such as rule-of-4, and display known active and inactive compounds for each PPI target. The DLiP aids the search for new candidate molecules for PPI drug discovery and is available online (https://skb-insilico.com/dlip).
Keywords: PMI; chemical library; database; drug design; physicochemical property; protein–protein interaction (PPI); rule-of-4.
Copyright © 2023 Ikeda, Maezawa, Yonezawa, Shimizu, Tashiro, Kanai, Sugaya, Masuda, Inoue, Niimi, Masuya, Mizuguchi, Furuya and Osawa.
Conflict of interest statement
Author YM was employed by the company Udzuki Inc., TT was employed by the company Lifematics Co., Ltd. and SK, NS, YoM, NI, TN, KM, and TF were employed by the company PeptiDream Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interface-aware molecular generative framework for protein-protein interaction modulators.J Cheminform. 2024 Dec 20;16(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13321-024-00930-0. J Cheminform. 2024. PMID: 39707457 Free PMC article.
-
Generating Potential Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitor Molecules Based on Physicochemical Properties.Molecules. 2023 Jul 26;28(15):5652. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155652. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570623 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Estimate Index for Early-Stage Screening of Compounds Targeting Protein-Protein Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 10;22(20):10925. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010925. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681589 Free PMC article.
-
Current Challenges and Opportunities in Designing Protein-Protein Interaction Targeted Drugs.Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2020 Nov 12;13:11-25. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S235542. eCollection 2020. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2020. PMID: 33209039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
iPPI-DB: a manually curated and interactive database of small non-peptide inhibitors of protein-protein interactions.Drug Discov Today. 2013 Oct;18(19-20):958-68. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 17. Drug Discov Today. 2013. PMID: 23688585 Review.
Cited by
-
DiPPI: A Curated Data Set for Drug-like Molecules in Protein-Protein Interfaces.J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Jul 8;64(13):5041-5051. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.3c01905. Epub 2024 Jun 22. J Chem Inf Model. 2024. PMID: 38907989 Free PMC article.
-
Chronological Analysis of First-in-Class Drugs Approved from 2011 to 2022: Their Technological Trend and Origin.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 22;15(7):1794. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071794. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37513981 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

