PoET: automated approach for measuring pore edge tension in giant unilamellar vesicles
- PMID: 36700098
- PMCID: PMC9710609
- DOI: 10.1093/bioadv/vbab037
PoET: automated approach for measuring pore edge tension in giant unilamellar vesicles
Abstract
Motivation: A reliable characterization of the membrane pore edge tension of single giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) requires the measurement of micrometer sized pores in hundreds to thousands of images. When manually performed, this procedure has shown to be extremely time-consuming and to generate inconsistent results among different users and imaging systems. A user-friendly software for such analysis allowing quick processing and generation of reproducible data had not yet been reported.
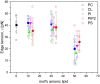
Results: We have developed a software (PoET) for automatic pore edge tension measurements on GUVs. The required image processing steps and the characterization of the pore dynamics are performed automatically within the software and its use allowed for a 30-fold reduction in the analysis time. We demonstrate the applicability of the software by comparing the pore edge tension of GUVs of different membrane compositions and surface charges. The approach was applied to electroporated GUVs but is applicable to other means of pore formation.
Availability and implementation: The complete software is implemented in Python and available for Windows at https://dx.doi.org/10.17617/3.7h.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics Advances online.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures



References
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L. et al. (2011) Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol., 29, 341–345. - PubMed
-
- Baumgart T. et al. (2003) Imaging coexisting fluid domains in biomembrane models coupling curvature and line tension. Nature, 425, 821–824. - PubMed
-
- Belehradek M. et al. (1993) Electrochemotherapy, a new antitumor treatment. First clinical phase I‐II trial. Cancer, 72, 3694–3700. - PubMed
-
- Bevers E. et al. (1996) Regulatory mechanisms in maintenance and modulation of transmembrane lipid asymmetry: pathophysiological implications. Lupus, 5, 480–487. - PubMed
-
- Brochard-Wyart F. et al. (2000) Transient pores in stretched vesicles: role of leak-out. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl., 278, 32–51.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

