Comparative Assessment of p16/Ki-67 Dual Staining Technology for cervical cancer screening in women living with HIV (COMPASS-DUST)-Study protocol
- PMID: 36701329
- PMCID: PMC9879465
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278077
Comparative Assessment of p16/Ki-67 Dual Staining Technology for cervical cancer screening in women living with HIV (COMPASS-DUST)-Study protocol
Abstract
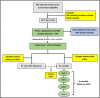
The risk of progression of low-grade (CIN1) to high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2/3) is 3-5 times higher for women living with HIV (WLHIV) than for HIV-negative women. Evidence suggests that the current cervical cancer screening methods perform less effectively in WLHIV. An emerging screening method-p16/Ki-67 dual staining technology (DUST) is a safe and rapid assay that could be used to detect CIN2/3 with higher sensitivity and specificity. The study in this protocol will evaluate the performance of DUST in cervical cancer screening among WLHIV. We will conduct an intra-participant comparative study (Phase 1) to enrol n = 1,123 sexually active WLHIV aged 25-65 years at two accredited adult HIV treatment centres in Lagos, Nigeria to compare the performance of DUST to the currently used screening methods (Pap smear, hr-HPV DNA, or VIA testing) in detecting high-grade CIN and cancer (CIN2+). Subsequently, a prospective cohort study (Phase 2) will be conducted by enrolling all the WLHIV who are diagnosed as having low-grade CIN (CIN1) in Phase 1 for a 6-monthly follow-up for 2 years to detect the persistence and progression of CIN1 to CIN2+. The findings of this study may provide evidence of the existence of a better performance screening method for the primary and triage detection of CIN2+ in WLHIV. It may also demonstrate that this high-performance test can improve the long-term predictive accuracy of screening by extending the intervals between evaluations and thus decrease the overall cost and increase screening uptake and follow-up compliance in WLHIV.
Copyright: © 2023 Okunade et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: KSO and GO are both editorial board members of PLoS One. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
References
-
- Smith DK, Neal JJ, Holmberg SD, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Idiopathic CD4+. From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1993 revised classification system for HIV infection and expanded surveillance case definition for AIDS among adolescents and adults. 1993.
-
- World Health Organisation. AIDS epidemic update. UNAIDS/WHO. 2004.