Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes of two alpine medicinal plants of Gentiana (Gentianaceae)
- PMID: 36701356
- PMCID: PMC9879513
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281134
Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes of two alpine medicinal plants of Gentiana (Gentianaceae)
Abstract
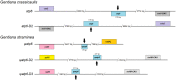
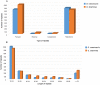
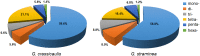
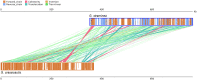
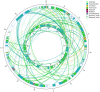
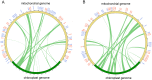
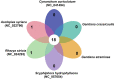
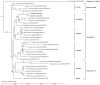
Gentiana crassicaulis and G. straminea are alpine plants of Gentiana with important medicinal value and complex genetic backgrounds. In this study, the mitochondrial genomes (mtDNAs) of these two species were sequenced. The mtDNAs of G. crassicaulis and G. straminea are 368,808 and 410,086 bp long, respectively, 52 and 49 unique genes are annotated in the two species, and the gene arrangement varies widely. Compared to G. crassicaulis, G. straminea loses three effective genes, namely atp6, trnG-GCC and trnV-GAC. As a pseudogene, the atp6 gene of G. straminea is incomplete, which is rare in higher plants. We detected 1696 and 1858 pairs of long repeats and 213 SSRs and 250 SSs in the mtDNAs of G. crassicaulis and G. straminea, respectively. There are 392 SNPs and 18 InDels between the two genomes, and syntenic sequence and structural variation analysis show low collinearity between the two genomes. Chloroplast DNA transferring to mtDNA is observed in both species, and 46,511 and 55,043 bp transferred segments containing three tRNA genes are identified, respectively. Comparative analysis of mtDNAs of G. crassicaulis, G. straminea and four species of Gentianales determined 18 core genes, and there is no specific gene in G. crassicaulis and G. straminea. The phylogenetic tree based on mtDNAs places Gentianaceae in a branch of Gentianales. This study is the first to analyze the mtDNAs of Gentianaceae, which could provide information for analysis of the structure of mtDNAs of higher plants and phylogenetic research of Gentianaceae and Gentianales.
Copyright: © 2023 Ala et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chloroplast genome structures in Gentiana (Gentianaceae), based on three medicinal alpine plants used in Tibetan herbal medicine.Curr Genet. 2017 May;63(2):241-252. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0631-1. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27422574
-
The complete chloroplast genome of Gentiana straminea (Gentianaceae), an endemic species to the Sino-Himalayan subregion.Gene. 2016 Feb 15;577(2):281-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26680100
-
The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Gentiana lawrencei var. farreri (Gentianaceae) and comparative analysis with its congeneric species.PeerJ. 2016 Sep 29;4:e2540. doi: 10.7717/peerj.2540. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 27703869 Free PMC article.
-
[DNA super-barcoding of several medicinal species in Gentiana from Yunnan province].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Oct;46(20):5260-5269. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210720.103. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34738428 Chinese.
-
Botany, traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control, and authentication of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae-A traditional medicine: A review.Phytomedicine. 2018 Jul 15;46:142-163. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.020. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30097114 Review.
Cited by
-
The first mitochondrial genome of Calophyllum soulattri Burm.f.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 1;14(1):5112. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55016-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38429360 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly and characterization of the first mitochondrial genome of Phyllanthaceae: a case study of the ornamental aquatic plant Phyllanthus fluitans.Genetica. 2025 Jul 16;153(1):25. doi: 10.1007/s10709-025-00241-8. Genetica. 2025. PMID: 40668455
-
Insights from the first chromosome-level genome assembly of the alpine gentian Gentiana straminea Maxim.DNA Res. 2024 Oct 1;31(5):dsae022. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsae022. DNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39017645 Free PMC article.
-
High-Quality Assembly and Analysis of the Complete Mitogenomes of German Chamomile (Matricaria recutita) and Roman Chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile).Genes (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;15(3):301. doi: 10.3390/genes15030301. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38540360 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly of the mitochondrial genome of Glycyrrhiza glabra and identification of two types of homologous recombination configurations caused by repeat sequences.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jan 6;26(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11190-5. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39762760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pan RZ, Wang XJ, Li NH. Phytophysiology. Higher Education Press, Beijing, China. 2012.
-
- Lu JN, Zhao ZL, Ni LH, Dorje G. Identification of medicinal plants based on mitochondrial DNA sequences. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs. 2016; 47(10):1791–1796. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2016.10.027 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

