A tissue-specific profile of miRNAs and their targets related to paeoniaflorin and monoterpenoids biosynthesis in Paeonia lactiflora Pall. by transcriptome, small RNAs and degradome sequencing
- PMID: 36701382
- PMCID: PMC9879538
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279992
A tissue-specific profile of miRNAs and their targets related to paeoniaflorin and monoterpenoids biosynthesis in Paeonia lactiflora Pall. by transcriptome, small RNAs and degradome sequencing
Abstract
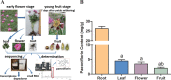
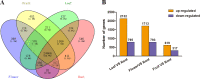
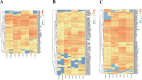
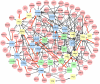
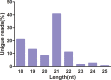
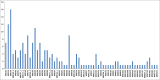
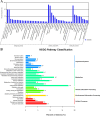
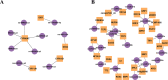
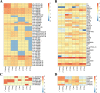
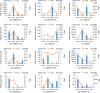
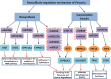
Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (Paeonia) has aroused many concerns due to its extensive medicinal value, in which monoterpene glucoside paeoniflorin and its derivatives are the active chemical components. However, little is known in the molecular mechanism of monoterpenoids biosynthesis, and the regulation network between small RNAs and mRNAs in monoterpenoids biosynthesis has not been investigated yet. Herein, we attempted to reveal the tissue-specific regulation network of miRNAs and their targets related to paeoniaflorin and monoterpenoids biosynthesis in Paeonia by combining mRNA and miRNA expression data with degradome analysis. In all, 289 miRNAs and 30177 unigenes were identified, of which nine miRNAs from seven miRNA families including miR396, miR393, miR835, miR1144, miR3638, miR5794 and miR9555 were verified as monoterpenoids biosynthesis-related miRNAs by degradome sequencing. Moreover, the co-expression network analysis showed that four monoterpenoids-regulating TFs, namely AP2, MYBC1, SPL12 and TCP2, were putatively regulated by five miRNAs including miR172, miR828, miR858, miR156 and miR319, respectively. The present study will improve our knowledge of the molecular mechanisms of the paeoniaflorin and monoterpenoids biosynthesis mediated by miRNA to a new level, and provide a valuable resource for further study on Paeonia.
Copyright: © 2023 Xu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Contents of paeoniflorin and albiflorin in two Korean landraces of Paeonia lactiflora and characterization of paeoniflorin biosynthesis genes in peony.Genes Genomics. 2024 Sep;46(9):1107-1122. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01553-3. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39126602
-
Multi-omics analysis of small RNA, transcriptome, and degradome to identify putative miRNAs linked to MeJA regulated and oridonin biosynthesis in Isodon rubescens.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Feb;258(Pt 2):129123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.129123. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38163496
-
Integration of Transcriptomes, Small RNAs, and Degradome Sequencing to Identify Putative miRNAs and Their Targets Related to Eu-Rubber Biosynthesis in Eucommia ulmoides.Genes (Basel). 2019 Aug 19;10(8):623. doi: 10.3390/genes10080623. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31430866 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal tissue-specific accumulation and expression patterns of monoterpene glycosides, gallaglycosides, and flavonoids in Paeonia Lactiflora Pall.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jun 4;26(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11750-3. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40468204 Free PMC article.
-
HpeNet: Co-expression Network Database for de novo Transcriptome Assembly of Paeonia lactiflora Pall.Front Genet. 2020 Oct 21;11:570138. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.570138. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33193666 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An efficient CRISPR-Cas12a-mediated MicroRNA knockout strategy in plants.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 Jan;23(1):128-140. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14484. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 39401095 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome, miRNA, and degradome sequencing reveal the leaf stripe (Pyrenophora graminea) resistance genes in Tibetan hulless barley.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jan 17;25(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06055-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39825242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang X, Wang J, Li X. A study on the chemical constituents of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. J Shenyang Pharm Univ. 2001;18: 30–32.
-
- Tan JJ, Zhao QC, Yang L, Shang ZP, Du ZQ, Yan M. Chemical constituents in roots of Paeonia lactiflora. Chinese Tradit Herb Drugs. 2010;41: 1245–1248.
-
- Dong H, Liu Z, Song F, Yu Z, Li H, Liu S. Structural analysis of monoterpene glycosides extracted from Paeonia lactiflora Pall. using electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom An Int J Devoted to Rapid Dissem Up-to-the-Minute Res Mass Spectrom. 2007;21: 3193–3199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

