Targeted Lymphoma Therapy Using a Gold Nanoframework-Based Drug Delivery System
- PMID: 36701696
- PMCID: PMC9911369
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c17214
Targeted Lymphoma Therapy Using a Gold Nanoframework-Based Drug Delivery System
Abstract
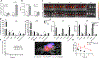
Precision nanomedicine can be employed as an alternative to chemo- or radiotherapy to overcome challenges associated with the often narrow therapeutic window of traditional treatment approaches, while safely inducing effective, targeted antitumor responses. Herein, we report the formulation of a therapeutic nanocomposite comprising a hyaluronic acid (HA)-coated gold nanoframework (AuNF) delivery system and encapsulated IT848, a small molecule with potent antilymphoma and -myeloma properties that targets the transcriptional activity of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). The porous AuNFs fabricated via a liposome-templated approach were loaded with IT848 and surface-functionalized with HA to formulate the nanotherapeutics that were able to efficiently deliver the payload with high specificity to myeloma and lymphoma cell lines in vitro. In vivo studies characterized biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and safety of HA-AuNFs, and we demonstrated superior efficacy of HA-AuNF-formulated IT848 vs free IT848 in lymphoma mouse models. Both in vitro and in vivo results affirm that the AuNF system can be adopted for targeted cancer therapy, improving the drug safety profile, and enhancing its efficacy with minimal dosing. HA-AuNF-formulated IT848 therefore has strong potential for clinical translation.
Keywords: CD44; gold nanoparticles; hyaluronic acid; lymphoma; nuclear factor-κB inhibitor; targeted drug delivery.
Figures


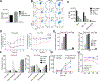


Similar articles
-
Facile strategy by hyaluronic acid functional carbon dot-doxorubicin nanoparticles for CD44 targeted drug delivery and enhanced breast cancer therapy.Int J Pharm. 2020 Mar 30;578:119122. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119122. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32035259
-
Hyaluronic acid shell and disulfide-crosslinked core micelles for in vivo targeted delivery of bortezomib for the treatment of multiple myeloma.Acta Biomater. 2018 Oct 15;80:288-295. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.022. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30240956
-
Inhibition of NF-κB DNA Binding Suppresses Myeloma Growth via Intracellular Redox and Tumor Microenvironment Modulation.Mol Cancer Ther. 2022 Dec 2;21(12):1798-1809. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-22-0257. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 36190955 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the applications of hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles for diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 Jul;14(4):e1799. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1799. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35485247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronic acid-modified liposomal honokiol nanocarrier: Enhance anti-metastasis and antitumor efficacy against breast cancer.Carbohydr Polym. 2020 May 1;235:115981. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115981. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Carbohydr Polym. 2020. PMID: 32122511 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in targeted drug delivery systems for multiple myeloma.J Control Release. 2024 Dec;376:215-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.10.003. Epub 2024 Oct 12. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 39384153 Review.
References
-
- Samal P; Begum S Drug Loaded Nanomaterials for Hematological Malignancies Diagnosis and Enhanced Targeted Therapy. In Advanced Nanomaterials for Point of Care Diagnosis and Therapy; Elsevier: 2022; pp 383–398.
-
- Powsner EH; Harris JC; Day ES Biomimetic Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Hematologic Malignancies. Advanced NanoBiomed Research 2021, 1 (4), 2000047.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

