Learning to stop responding
- PMID: 36702436
- PMCID: PMC10495103
- DOI: 10.1016/j.beproc.2023.104830
Learning to stop responding
Abstract
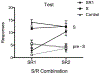
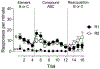
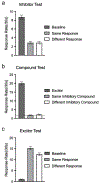
Learning to stop responding is an important process that allows behavior to adapt to a changing and variable environment. This article reviews recent research in this laboratory and others that has studied how animals learn to stop responding in operant extinction, punishment, and feature-negative learning. Extinction and punishment are shown to be similar in two fundamental ways. First, the response-suppressing effects of both are highly context-specific. Second, the response-suppressing effects of both can be remarkably response-specific: Inhibition of one response transfers little to other responses. Learning to inhibit the response so specifically may result from the correction of "response error," the difference between the level of responding and what the current reinforcer supports. In contrast, the inhibition of responding that develops in feature-negative learning, where the response is reinforced during one discriminative stimulus (A) but not in a compound of A and stimulus B, is less response-specific: The inhibition of responding by stimulus B transfers and inhibits a second response, especially if the second response has itself been inhibited before. The results thus indicate both response-specific and response-general forms of behavioral inhibition. One possibility is that response-specific inhibition is learned when the circumstances encourage the organism to pay attention to the response-to what it is actually doing-as behavioral suppression is learned.
Keywords: Extinction; Feature-negative learning; Operant behavior; Punishment; Response inhibition.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
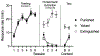
Similar articles
-
Infralimbic cortex plays a similar role in the punishment and extinction of instrumental behavior.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2024 May;211:107926. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2024.107926. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2024. PMID: 38579897 Free PMC article.
-
Correction of response error versus stimulus error in the extinction of discriminated operant learning.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2020 Oct;46(4):398-407. doi: 10.1037/xan0000267. Epub 2020 Jul 27. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2020. PMID: 32718156 Free PMC article.
-
Renewal after the punishment of free operant behavior.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2015 Jan;41(1):81-90. doi: 10.1037/xan0000051. Epub 2014 Dec 1. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2015. PMID: 25706548 Free PMC article.
-
A fundamental role for context in instrumental learning and extinction.Behav Processes. 2014 May;104:13-9. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2014.02.012. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Behav Processes. 2014. PMID: 24576702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extinction of instrumental (operant) learning: interference, varieties of context, and mechanisms of contextual control.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):7-19. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5076-4. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30350221 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Partial reinforcement extinction and omission effects in the elimination and recovery of discriminated operant behavior.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2023 Jul;49(3):194-207. doi: 10.1037/xan0000354. Epub 2023 Jun 1. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2023. PMID: 37261748 Free PMC article.
-
The temporal structure of goal-directed and habitual operant behavior.J Exp Anal Behav. 2024 Jan;121(1):38-51. doi: 10.1002/jeab.896. Epub 2023 Dec 22. J Exp Anal Behav. 2024. PMID: 38131488 Free PMC article.
-
A Mixed-Method Analytical Cross-Sectional Research of Person-Centered Learning Behaviors Among Adolescent and Adult Learners.Cureus. 2024 May 30;16(5):e61398. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61398. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38953062 Free PMC article.
-
Response-specific effects of punishment of a discriminated operant response.Learn Motiv. 2023 Aug;83:101907. doi: 10.1016/j.lmot.2023.101907. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Learn Motiv. 2023. PMID: 37484761 Free PMC article.
-
Infralimbic cortex plays a similar role in the punishment and extinction of instrumental behavior.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2024 May;211:107926. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2024.107926. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2024. PMID: 38579897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker AG, Steinwald H, & Bouton ME (1991). Contextual conditioning and reinstatement of extinguished instrumental responding. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section B, 43(2), 199–218.
-
- Bolles RC (1972). Reinforcement, expectancy, and learning. Psychological Review, 79(5), 394–409.
-
- Bolles RC, Holtz R, Dunn T, & Hill W (1980). Comparisons of stimulus learning and response learning in a punishment situation. Learning and Motivation, 11, 78–96.
-
- Bonardi C (1989). Inhibitory discriminative control is specific to both the response and the reinforcer. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology Section B, 41(3), 225–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

