Coenzyme Q biochemistry and biosynthesis
- PMID: 36702698
- PMCID: PMC10106368
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.12.006
Coenzyme Q biochemistry and biosynthesis
Abstract
Coenzyme Q (CoQ) is a remarkably hydrophobic, redox-active lipid that empowers diverse cellular processes. Although most known for shuttling electrons between mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) complexes, the roles for CoQ are far more wide-reaching and ever-expanding. CoQ serves as a conduit for electrons from myriad pathways to enter the ETC, acts as a cofactor for biosynthetic and catabolic reactions, detoxifies damaging lipid species, and engages in cellular signaling and oxygen sensing. Many open questions remain regarding the biosynthesis, transport, and metabolism of CoQ, which hinders our ability to treat human CoQ deficiency. Here, we recount progress in filling these knowledge gaps, highlight unanswered questions, and underscore the need for novel tools to enable discoveries and improve the treatment of CoQ-related diseases.
Keywords: coenzyme Q; complex Q; lipids; mitochondria; oxidative phosphorylation; ubiquinone.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests None are declared by the authors.
Figures
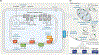
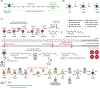
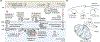


References
-
- Crane FL et al. (1957) Isolation of a quinone from beef heart mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 25, 220–221 - PubMed
-
- Morton RA (1958) Ubiquinone. Nature 182, 1764–1767 - PubMed
-
- Baschiera E et al. (2021) The multiple roles of coenzyme Q in cellular homeostasis and their relevance for the pathogenesis of coenzyme Q deficiency. Free Radical Bio Med 166, 277–286 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

