Adaptive resistance to lorlatinib via EGFR signaling in ALK-rearranged lung cancer
- PMID: 36702855
- PMCID: PMC9879975
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-023-00350-7
Adaptive resistance to lorlatinib via EGFR signaling in ALK-rearranged lung cancer
Abstract
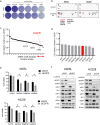
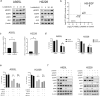
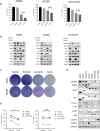
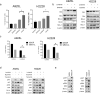
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors rarely elicit complete responses in patients with advanced ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as a small population of tumor cells survives due to adaptive resistance. Therefore, we focused on the mechanisms underlying adaptive resistance to lorlatinib and therapeutic strategies required to overcome them. We found that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling was involved in the adaptive resistance to lorlatinib in ALK-rearranged NSCLC, activation of which was induced by heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor production via c-Jun activation. EGFR inhibition halted ALK-rearranged lung cancer cell proliferation by enhancing ALK inhibition-induced apoptosis via suppression of Bcl-xL. Xenograft models showed that the combination of EGFR inhibitor and lorlatinib considerably suppressed tumor regrowth following cessation of these treatments. This study provides new insights regarding tumor evolution due to EGFR signaling after lorlatinib treatment and the development of combined therapeutic strategies for ALK-rearranged lung cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.Y. received commercial research grants from Pfizer, Ono Pharmaceutical, Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., AstraZeneca, and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited and has received speaking honoraria from Eli Lilly. R.K. received research grants from Chugai, Takeda, and TOPPAN outside the submitted work. K. Takayama received research grants from Chugai-Roche and Ono Pharmaceutical and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai-Roche, MSD-Merck, Eli Lilly, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and Daiichi-Sankyo. The other authors disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling increased apoptosis and prevented the emergence of ALK-TKI-tolerant cells in ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Lett. 2021 Dec 1;522:119-128. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.09.018. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 34534615
-
Pan-HER inhibitors overcome lorlatinib resistance caused by NRG1/HER3 activation in ALK-rearranged lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2023 Jan;114(1):164-173. doi: 10.1111/cas.15579. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36086904 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 inhibition suppresses adaptive survival of ALK-rearranged lung cancer cells through transcriptional modulation of apoptosis.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2022 Feb 28;6(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s41698-022-00254-y. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35228642 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and clinical properties of lorlatinib in the treatment of ALK-rearranged advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;21(13):1547-1554. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1774552. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32511029 Review.
-
Spotlight on lorlatinib and its potential in the treatment of NSCLC: the evidence to date.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Aug 22;11:5093-5101. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S165511. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30174447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Development to Place in Therapy of Lorlatinib for the Treatment of ALK and ROS1 Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 25;14(1):48. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14010048. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting ERBB3 and AKT to overcome adaptive resistance in EML4-ALK-driven non-small cell lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Dec 18;15(12):912. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07272-7. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39695132 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired RUFY1-RET rearrangement as a mechanism of resistance to lorlatinib in a patient with CD74-ROS1 rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: A case report.Oncotarget. 2025 Feb 5;16:39-42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28682. Oncotarget. 2025. PMID: 39907599 Free PMC article.
-
HER3 overexpression: a predictive marker for poor prognosis in advanced ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer treated with ALK inhibitors.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 29;13(2):321-333. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-804. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38496685 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of drug-tolerant persister cells as an approach to counter drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2024 Aug;194:107885. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2024.107885. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Lung Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39002493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lin JJ, Riely GJ, Shaw AT. Targeting ALK: Precision medicine takes on drug resistance. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:137–155. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-1123. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

