Ferroptosis in colorectal cancer: a future target?
- PMID: 36703079
- PMCID: PMC10070248
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-023-02149-6
Ferroptosis in colorectal cancer: a future target?
Abstract
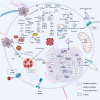
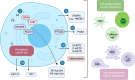
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide and is characterised by frequently mutated genes, such as APC, TP53, KRAS and BRAF. The current treatment options of chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery are met with challenges such as cancer recurrence, drug resistance, and overt toxicity. CRC therapies exert their efficacy against cancer cells by activating biological pathways that contribute to various forms of regulated cell death (RCD). In 2012, ferroptosis was discovered as an iron-dependent and lipid peroxide-driven form of RCD. Recent studies suggest that therapies which target ferroptosis are promising treatment strategies for CRC. However, a greater understanding of the mechanisms of ferroptosis initiation, propagation, and resistance in CRC is needed. This review provides an overview of recent research in ferroptosis and its potential role as a therapeutic target in CRC. We also propose future research directions that could help to enhance our understanding of ferroptosis in CRC.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic efficacy of ferroptosis in the treatment of colorectal cancer (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 Sep 26;28(6):563. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14697. eCollection 2024 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39390976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Ferroptosis to Overcome Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer: Promising Therapeutic Approaches.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 30;15(21):5209. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215209. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis: the balance between death and survival in colorectal cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jul 2;20(10):3773-3783. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.96828. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39113707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis Plays a Pivotal Role in Activating and Modulating Specific Intracellular Signaling Pathways Integrated into the Therapeutic Management of Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Cell Med. 2024;13(4):374-386. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.13.4.374. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2024. PMID: 39895914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights on Ferroptosis and Colorectal Cancer: Progress and Updates.Molecules. 2022 Dec 28;28(1):243. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010243. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615434 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic accuracy of magnifying chromoendoscopy in the assessment of tumor invasion depth in early colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Tech Coloproctol. 2023 Dec;27(12):1155-1167. doi: 10.1007/s10151-023-02833-y. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Tech Coloproctol. 2023. PMID: 37474693
-
A novel antitumor mechanism of triptonide in colorectal cancer: inducing ferroptosis via the SLC7A11/GPX4 axis.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Jul 16;24(4):126. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01402-2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39012393
-
LINC01232 promotes ARNTL2 transcriptional activation and inhibits ferroptosis of CRC cells through p300/H3K27ac.Epigenomics. 2024;16(15-16):1097-1115. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2024.2387528. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Epigenomics. 2024. PMID: 39268727
-
Association between serum iron status and the risk of colorectal cancer in US adults: a cross-sectional analysis of NHANES 2001-2020.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 3;24(1):449. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03540-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39627699 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of decreased ferroptosis in male colorectal cancer patients with KRAS mutations.Redox Biol. 2023 Jun;62:102699. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102699. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37086630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

