The impact of caregiving on quality of life in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review
- PMID: 36703272
- PMCID: PMC10214089
- DOI: 10.1002/gps.5870
The impact of caregiving on quality of life in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review
Abstract
Objective: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that can reduce quality of life (QOL). Previous research has explored patient specific factors that influence QOL; but understanding external factors that may also affect patient QOL, such as caregiver characteristics, can provide additional intervention targets that may improve QOL for both the person with PD and their caregiver.
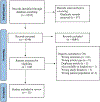
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of existing literature on caregiver factors that are related to QOL for the person with PD. We developed a tailored search strategy in six databases and performed a screening procedure according to PRISMA guidelines. We synthesized findings from articles that met inclusion criteria using a narrative approach and identified themes categorizing caregiver factors associated with PD QOL.
Results: We found 32 full-text articles that fulfilled the inclusion criteria and passed the quality appraisal. Seven themes were identified, including: (1) burden, (2) strain, (3) QOL and satisfaction, (4) demographic factors, (5) psychological factors, (6) relationship factors, and (7) caregiver input.
Conclusions: Our review presents critical insights into the role of the caregiver in the QOL of a person with PD. Findings reveal several targets for intervention to improve QOL in this population.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; burden; caregiver; quality of life; strain.
© 2023 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Saxena S, Saraceno B. WHOQOL User Manual. World Health Organization; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous