The role of lncRNAs/miRNAs/Sirt1 axis in myocardial and cerebral injury
- PMID: 36703306
- PMCID: PMC10081082
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2172265
The role of lncRNAs/miRNAs/Sirt1 axis in myocardial and cerebral injury
Abstract
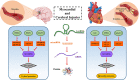
In recent years, researchers have begun to realize the importance of the role of non-coding RNAs in the treatment of cancer and cardiovascular and neurological diseases. LncRNAs and miRNAs are important non-coding RNAs, which regulate gene expression and activate mRNA translation through binding to diverse target sites. Their involvement in the regulation of protein function and the modulation of physiological and pathological conditions continues to be investigated. Sirtuins, especially Sirt1, have a critical function in regulating a variety of physiological processes such as oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy. The lncRNAs/miRNAs/Sirt1 axis may be a novel regulatory mechanism, which is involved in the progression and/or prevention of numerous diseases. This review focuses on recent findings on the crosstalk between non-coding RNAs and Sirt1 in myocardial and cerebral injuries and may provide some insight into the development of novel approaches in the treatment of these disorders.Abbreviation: BMECs, brain microvascular endothelial cells; C2dat1, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit delta (CAMK2D)-associated transcript 1; EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; FOXOs, forkhead transcription factors; GAS5, growth arrest-specific 5; HAECs, human aortic endothelial cells; HAND2-AS1, HAND2 Antisense RNA 1; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; ILF3-AS1, interleukin enhancer-binding factor 3-antisense RNA 1; KLF3-AS1, KLF3 antisense RNA 1; LncRNA, long noncoding RNA; LUADT1, Lung Adenocarcinoma Associated Transcript 1; MALAT1, Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; miRNA, microRNA; NEAT1, nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; OIP5-AS1, Opa-interacting protein 5-antisense transcript 1; Sirt1-AS, Sirt1 Antisense RNA; SNHG7, small nucleolar RNA host gene 7; SNHG8, small nucleolar RNA host gene 8; SNHG12, small nucleolar RNA host gene 12; SNHG15, small nucleolar RNA host gene 15; STAT3, signal transducers and activators of transcription 3; TUG1, taurine up-regulated gene 1; VSMCs, vascular smooth muscle cells; XIST, X inactive specific transcript; ZFAS1, ZNFX1 Antisense RNA 1.
Keywords: ANRIL; MALAT1; Non-coding RNA; atherosclerosis; ischemia; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016. Jan 26;133:e38–360. - PubMed
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, et al. heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020. Mar 3;141:e139–596. - PubMed
-
- Joseph P, Leong D, McKee M, et al. Reducing the global burden of cardiovascular disease, Part 1: the epidemiology and risk factors. Circ Res. 2017. Sep 1;121:677–694. - PubMed
-
- Radu RA, Terecoasă EO, Băjenaru OA, et al. Etiologic classification of ischemic stroke: where do we stand? Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017. Aug;159:93–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
