Linking graphene-based material physicochemical properties with molecular adsorption, structure and cell fate
- PMID: 36703309
- PMCID: PMC9814659
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-019-0254-9
Linking graphene-based material physicochemical properties with molecular adsorption, structure and cell fate
Abstract
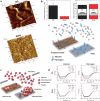
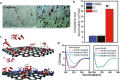
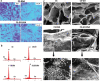
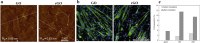
Graphene, an allotrope of carbon, consists of a single layer of carbon atoms with uniquely tuneable properties. As such, graphene-based materials (GBMs) have gained interest for tissue engineering applications. GBMs are often discussed in the context of how different physicochemical properties affect cell physiology, without explicitly considering the impact of adsorbed proteins. Establishing a relationship between graphene properties, adsorbed proteins, and cell response is necessary as these proteins provide the surface upon which cells attach and grow. This review highlights the molecular adsorption of proteins on different GBMs, protein structural changes, and the connection to cellular function.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular Control of Interfacial Fibronectin Structure on Graphene Oxide Steers Cell Fate.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Jan 20;13(2):2346-2359. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c21042. Epub 2021 Jan 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33412842
-
Graphene Surfaces Interaction with Proteins, Bacteria, Mammalian Cells, and Blood Constituents: The Impact of Graphene Platelet Oxidation and Thickness.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 May 6;12(18):21020-21035. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b21841. Epub 2020 Apr 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32233456
-
Preparation, properties, applications and outlook of graphene-based materials in biomedical field: a comprehensive review.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2023 Jun;34(8):1121-1156. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2022.2155781. Epub 2022 Dec 15. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2023. PMID: 36475416 Review.
-
Graphene-Based Material-Mediated Immunomodulation in Tissue Engineering and Regeneration: Mechanism and Significance.ACS Nano. 2023 Oct 10;17(19):18669-18687. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03857. Epub 2023 Sep 28. ACS Nano. 2023. PMID: 37768738 Review.
-
Environmental biotechnology and the involving biological process using graphene-based biocompatible material.Chemosphere. 2023 Oct;339:139771. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139771. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Chemosphere. 2023. PMID: 37567262
Cited by
-
Modulation of Conductivity of Alginate Hydrogels Containing Reduced Graphene Oxide through the Addition of Proteins.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 15;13(9):1473. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091473. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575549 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Albumin Isolation from Human Serum with Graphene Oxide and Derivatives: A Novel Approach for Clinical Applications.ACS Omega. 2024 Sep 20;9(39):40592-40607. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c04276. eCollection 2024 Oct 1. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39371982 Free PMC article.
-
Graphene Hybrid Materials for Controlling Cellular Microenvironments.Materials (Basel). 2020 Sep 10;13(18):4008. doi: 10.3390/ma13184008. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32927729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First-Principles Calculations for Glycine Adsorption Dynamics and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy on Diamond Surfaces.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Mar 27;15(7):502. doi: 10.3390/nano15070502. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40214547 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterials Mimicking Mechanobiology: A Specific Design for a Specific Biological Application.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 26;25(19):10386. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910386. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Wu C, Guo S, Zhang J. Interactions of graphene and graphene oxide with proteins and peptides. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2013;2:27–45. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2012-0078. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

