N-Terminal selective modification of peptides and proteins using 2-ethynylbenzaldehydes
- PMID: 36703438
- PMCID: PMC9814395
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-020-0309-y
N-Terminal selective modification of peptides and proteins using 2-ethynylbenzaldehydes
Abstract
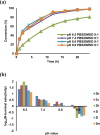
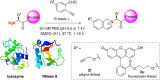
Selective modification of the N-terminus of peptides and proteins is a promising strategy for single site modification methods. Here we report N-terminal selective modification of peptides and proteins by using 2-ethynylbenzaldehydes (2-EBA) for the production of well-defined bioconjugates. After reaction screening with a series of 2-EBA, excellent N-terminal selectivity is achieved by the reaction in slightly acidic phosphate-buffered saline using 2-EBA with electron-donating substituents. Selective modification of a library of peptides XSKFR (X = either one of 20 natural amino acids) by 2-ethynyl-4-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde (2d) results in good-to-excellent N-terminal selectivity in peptides (up to >99:1). Lysozyme, ribonuclease A and a therapeutic recombinant Bacillus caldovelox arginase mutant (BCArg mutant) are N-terminally modified using alkyne- and fluorescein-linked 2-EBA. Alkyne-linked BCArg mutant is further modified by rhodamine azide via copper(I)-catalyzed [3 + 2] cycloaddition indicating that the reaction has high functional group compatibility. Moreover, the BCArg mutant modified by 2-ethynyl-5-methoxybenzaldehyde (2b) exhibits comparable activity in enzymatic and cytotoxic assays with the unmodified one.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: M.-K.W. has filed a patent application on the use of 2-ethynylbenzaldehydes for bioconjugation (WO2019219002) and all other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Modification of N-terminal α-amino groups of peptides and proteins using ketenes.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Feb 8;134(5):2589-98. doi: 10.1021/ja208009r. Epub 2012 Jan 30. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22288779
-
Functionalized quinolizinium-based fluorescent reagents for modification of cysteine-containing peptides and proteins.RSC Adv. 2022 Feb 22;12(10):6248-6254. doi: 10.1039/d1ra08329e. eCollection 2022 Feb 16. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35424586 Free PMC article.
-
Selective modification of alkyne-linked peptides and proteins by cyclometalated gold(III) (C^N) complex-mediated alkynylation.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Apr 1;28(7):115375. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115375. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32122753
-
Click to join peptides/proteins together.Chem Asian J. 2011 Oct 4;6(10):2606-16. doi: 10.1002/asia.201100329. Chem Asian J. 2011. PMID: 22043498 Review.
-
Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC)-Mediated Macrocyclization of Peptides: Impact on Conformation and Biological Activity.Curr Top Med Chem. 2018;18(7):591-610. doi: 10.2174/1568026618666180518095755. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29773065 Review.
Cited by
-
N-terminal truncated phospholipase A1 accessory protein PlaS from Serratia marcescens alleviates inhibitory on host cell growth and enhances PlaA1 enzymatic activity.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2024 Jun 25;11(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s40643-024-00777-1. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2024. PMID: 38916814 Free PMC article.
-
Isochromene and Dihydroisobenzofuran Electrosynthesis by a Highly Regiodivergent Cyclization of 2-Ethynylbenzaldehydes.J Org Chem. 2025 Jul 11;90(27):9532-9540. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5c00967. Epub 2025 Jun 29. J Org Chem. 2025. PMID: 40583244 Free PMC article.
-
Direct N- or C-Terminal Protein Labeling Via a Sortase-Mediated Swapping Approach.Bioconjug Chem. 2021 Nov 17;32(11):2397-2406. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.1c00442. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Bioconjug Chem. 2021. PMID: 34748323 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Bioorthogonal Ligation and Bioconjugation.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2023 Nov 22;381(6):35. doi: 10.1007/s41061-023-00445-6. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2023. PMID: 37991570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Protein N-Terminus for Site-Specific Bioconjugation.Molecules. 2021 Jun 9;26(12):3521. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123521. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34207845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

