Comparing the Efficacy of Premedication with Ibuprofen in Combination with an Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block and Primary Buccal Infiltration in Mandibular Molars with Irreversible Pulpitis: A Triple-blinded Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 36703687
- PMCID: PMC9868997
- DOI: 10.22037/iej.v17i4.37438
Comparing the Efficacy of Premedication with Ibuprofen in Combination with an Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block and Primary Buccal Infiltration in Mandibular Molars with Irreversible Pulpitis: A Triple-blinded Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
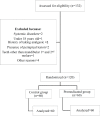
Introduction: This study aimed to determine the success rate of the combination of buccal infiltration (BI) and inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB) injections in irreversible pulpitis in mandibular molars after premedication with ibuprofen.
Materials and methods: From 132 patients participated in the study, 120 patients were included. One hour before root canal treatment, patients with mandibular molars with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis received either a 600 mg ibuprofen capsule or a placebo. All patients received 2% lidocaine with 1:80000 epinephrine and 4% articaine with 1:100000 epinephrine for IANB and BI, respectively. Patients' pain was evaluated using the Heft-Parker visual analog scale during the preparation of access cavity, exposure of pulp, and instrumentation of root canal. The success of anesthesia was defined as the absence of pain or mild pain. The Chi-square and t-test were employed for data analysis.
Results: The difference between patient age and gender in the two groups was not significant (P>0.05). The anesthesia success rate was 85% in the premedicated and 70% in the placebo group, with statistically significant results (P=0.049).
Conclusion: Based on this triple-blinded randomized clinical study, mandibular molars with irreversible pulpitis were not thoroughly anesthetized by a combination of IANB+BI after premedication with ibuprofen (600 mg), even though anesthesia success was improved significantly by ibuprofen premedication.
Keywords: Anesthesia; Buccal Infiltration; Ibuprofen; Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block; Placebo; Premedication.
Conflict of interest statement
‘None declared’.
Similar articles
-
Evaluating Combined Effect of Oral Premedication with Ibuprofen and Dexamethasone on Success of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block in Mandibular Molars with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis: A Prospective, Double-blind, Randomized Clinical Trial.J Endod. 2021 May;47(5):705-710. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2021.01.005. Epub 2021 Feb 4. J Endod. 2021. PMID: 33548329 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative evaluation of anesthetic efficacy of inferior alveolar nerve block and inferior alveolar nerve block plus buccal or lingual infiltration using articaine in mandibular molars with irreversible pulpitis: a preliminary prospective randomized single-blind clinical trial.Quintessence Int. 2021 Sep 9;52(9):820-826. doi: 10.3290/j.qi.b1864321. Quintessence Int. 2021. PMID: 34369941 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of oral premedication of meloxicam, ketorolac, dexamethasone, and ibuprofen on the success rate of inferior alveolar nerve block in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial.Quintessence Int. 2023 Feb 10;54(2):92-99. doi: 10.3290/j.qi.b3605097. Quintessence Int. 2023. PMID: 36421046 Clinical Trial.
-
Can 4% Articaine Buccal Infiltration Replace Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block (IANB) with 2% Xylocaine for Pulp Therapy in Primary Mandibular Molars? A Systematic Review.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021 May-Jun;14(3):420-425. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1974. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021. PMID: 34720518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of premedication on the success of inferior alveolar nerve block in patients diagnosed with irreversible pulpitis: An umbrella review.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2023 Jun 27;20:75. eCollection 2023. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2023. PMID: 37483905 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Efficacy of Analgesics for Pain Relief in Patients with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis Prior to Emergency Endodontic Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Iran Endod J. 2023;18(4):194-201. doi: 10.22037/iej.v18i4.35469. Iran Endod J. 2023. PMID: 37829826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parirokh M, Rekabi AR, Ashouri R, Nakhaee N, Abbott PV, Gorjestani H. Effect of occlusal reduction on postoperative pain in teeth with irreversible pulpitis and mild tenderness to percussion. J Endod. 2013;39(1):1–5. - PubMed
-
- Moradi Askari E, Parirokh M, Nakhaee N, Hosseini HR, Abbott PV. The effect of maxillary first molar root length on the success rate of buccal infiltration anesthesia. J Endod. 2016;42(10):1462–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources