Human Treated Dentin Matrix Hydrogel as a Drug Delivery Scaffold for Regenerative Endodontics
- PMID: 36703697
- PMCID: PMC9868998
- DOI: 10.22037/iej.v17i4.35580
Human Treated Dentin Matrix Hydrogel as a Drug Delivery Scaffold for Regenerative Endodontics
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of the current study was to develop a human treated dentin matrix (hTDM) hydrogel for use as a scaffold to allow the controlled release of an antimicrobial agent for regenerative endodontics.
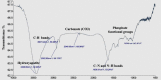
Materials and methods: Human extracted teeth were treated via chemical demineralization using ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid solution to produce hTDM powder. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was conducted to determine the functional groups of hTDM, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to define the morphology/particle size of hTDM, and energy dispersive X-ray analysis was performed to identify the superficial apatite groups. Prepared hTDM powder was added to the amoxicillin-clavulanate mixture with a mass ratio of 1:1. Then, the combination was dripped into a 5% (w/v) calcium chloride solution. Antibiotic release profiles were evaluated for 14 days via high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Hydrogel degradation properties were studied for 14 days using 10 mL of phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Encapsulation efficiency was determined by HPLC, while minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of amoxicillin-clavulanate were determined against Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis). The antibacterial activity of amoxicillin-clavulanate against E. faecalis was investigated for 14 days via agar diffusion test. Statistical analysis was performed with the Shapiro-Wilk test (P=0.05).
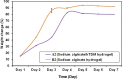
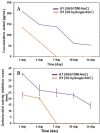
Results: hTDM showed statistically a significant difference for percentage weight change (P=0.1). The encapsulation efficiencies for hTDM hydrogel with antibiotic and hydrogel with antibiotic was 96.08%±0.02 and 94.62%±0.11, respectively. MIC and MBC values of amoxicillin-clavulanate against E. faecalis were 2.4 µg/mL and 9.6 µg/mL, respectively. The antibacterial activity of antibiotic loaded hTDM hydrogels was significantly greater than loaded hydrogels alone by 31% after 4 days and 100% at 14 days, respectively (P≤0.001).
Conclusions: This in vitro study showed antibiotic-loaded injectable hTDM hydrogel could be an alternative system to transfer antibiotic-based intracanal medicaments for use in regenerative endodontics.
Keywords: Demineralized Dentin Matrix; Drug Delivery Systems; Hydrogels; Regenerative Endodontics.
Figures

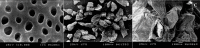

Similar articles
-
Effect of allicin-incorporated graphene oxide hydrogel on dentin microhardness.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Mar 30;25(1):461. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05870-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40159491 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Antibacterial Efficacy of Triple Antibiotic-Loaded Hydrogel Versus Modified Triple Antibiotic-Loaded Hydrogel as Intracanal Medicament Against Enterococcus faecalis: An In vitro Study.Eur Endod J. 2024 Mar;9(2):154-160. doi: 10.14744/eej.2023.06977. Eur Endod J. 2024. PMID: 38456465 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of osteogenic potential of demineralized dentin matrix hydrogel for bone formation.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Apr 28;23(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-02928-w. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37118728 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity and Biocompatibility of Antibiotic-Loaded Chitosan Hydrogels as a Potential Scaffold in Regenerative Endodontic Treatment.J Endod. 2020 Dec;46(12):1867-1875. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2020.09.007. Epub 2020 Sep 15. J Endod. 2020. PMID: 32941892
-
Photocrosslinkable methacrylated gelatin hydrogel as a cell-friendly injectable delivery system for chlorhexidine in regenerative endodontics.Dent Mater. 2022 Sep;38(9):1507-1517. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2022.07.002. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Dent Mater. 2022. PMID: 35882570 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the osteogenic effects of demineralized dentin matrix and acellular dentin matrix.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 1;42(1):28-36. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2023.2023161. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38475948 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Photocrosslinkable gelatin-treated dentin matrix hydrogel as a novel pulp capping agent for dentin regeneration: I. synthesis, characterizations and grafting optimization.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Aug 4;23(1):536. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03236-z. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37542230 Free PMC article.
-
Histological evaluation of the regenerative potential of a novel photocrosslinkable gelatin-treated dentin matrix hydrogel in direct pulp capping: an animal study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jan 19;24(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-03868-9. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38243218 Free PMC article.
-
Histomorphometric and immunohistochemical assessment of treated dentin matrix delivered by platelet-rich fibrin for socket preservation in rabbit model.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Feb 12;25(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05569-3. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 39939950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silva JS, Marques-da-Silva D, Lagoa R. Towards the Development of Delivery Systems of Bioactive Compounds With Eyes Set on Pharmacokinetics. Modeling and Control of Drug Delivery Systems. Elsevier; 2021. pp. 125–144.
-
- Mueller B, Treccani L, Rezwan K. Antibacterial active open-porous hydroxyapatite/lysozyme scaffolds suitable as bone graft and depot for localized drug delivery. J. Biomater. 2017;31(8):1123–34. - PubMed
-
- Soriano-Souza CA, Rossi AL, Mavropoulos E, Hausen MA, Tanaka MN, Calasans-Maia MD, et al. Chlorhexidine-loaded hydroxyapatite microspheres as an antimicrobial delivery system and its effect on in vivo osteoconductive properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 2015;26(4):166. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
