The Drosophila-parasitizing wasp Leptopilina heterotoma: A comprehensive model system in ecology and evolution
- PMID: 36703713
- PMCID: PMC9871341
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.9625
The Drosophila-parasitizing wasp Leptopilina heterotoma: A comprehensive model system in ecology and evolution
Abstract
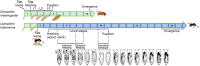
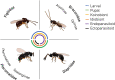
The parasitoid Leptopilina heterotoma has been used as a model system for more than 70 years, contributing greatly to diverse research areas in ecology and evolution. Here, we synthesized the large body of work on L. heterotoma with the aim to identify new research avenues that could be of interest also for researchers studying other parasitoids and insects. We start our review with a description of typical L. heterotoma characteristics, as well as that of the higher taxonomic groups to which this species belongs. We then continue discussing host suitability and immunity, foraging behaviors, as well as fat accumulation and life histories. We subsequently shift our focus towards parasitoid-parasitoid interactions, including L. heterotoma coexistence within the larger guild of Drosophila parasitoids, chemical communication, as well as mating and population structuring. We conclude our review by highlighting the assets of L. heterotoma as a model system, including its intermediate life history syndromes, the ease of observing and collecting natural hosts and wasps, as well as recent genomic advances.
Keywords: associative learning; endosymbiont; fitness; host‐parasitoid community; lipids; sex pheromones; virulence.
© 2023 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Partial venom gland transcriptome of a Drosophila parasitoid wasp, Leptopilina heterotoma, reveals novel and shared bioactive profiles with stinging Hymenoptera.Gene. 2013 Sep 10;526(2):195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.04.080. Epub 2013 May 17. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23688557 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Suppressive Extracellular Vesicle Proteins of Leptopilina heterotoma Are Encoded in the Wasp Genome.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Jan 7;10(1):1-12. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400349. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 31676506 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological and genetic interactions in Drosophila-parasitoids communities: a case study with D. melanogaster, D. simulans and their common Leptopilina parasitoids in south-eastern France.Genetica. 2004 Mar;120(1-3):181-94. doi: 10.1023/b:gene.0000017640.78087.9e. Genetica. 2004. PMID: 15088657
-
Ecology and life history evolution of frugivorous Drosophila parasitoids.Adv Parasitol. 2009;70:3-44. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(09)70001-6. Adv Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19773065 Review.
-
Drosophila Cellular Immunity Against Parasitoid Wasps: A Complex and Time-Dependent Process.Front Physiol. 2019 May 15;10:603. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00603. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31156469 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Many parasitoids lack adult fat accumulation, despite fatty acid synthesis: A discussion of concepts and considerations for future research.Curr Res Insect Sci. 2023 Mar 30;3:100055. doi: 10.1016/j.cris.2023.100055. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Insect Sci. 2023. PMID: 37124650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strength of enemy release from parasitoids is context-dependent in the invasive African Fig Fly, Zaprionus indianus.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 27:2024.07.09.602257. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.09.602257. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Ecol Evol. 2025 Mar 13;15(3):e70754. doi: 10.1002/ece3.70754. PMID: 39026893 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Flies use acetic acid to protect their offspring from parasitoids.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Aug 11;21(8):e1013368. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013368. eCollection 2025 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40788947 Free PMC article.
-
Defensive tactics: lessons from Drosophila.Biol Open. 2024 Dec 15;13(12):bio061609. doi: 10.1242/bio.061609. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 39718046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Immunity in Insects: The Lights and Shadows of Phenoloxidase System Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 4;26(3):1320. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031320. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941087 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abram, P. K. , Wang, X. , Hueppelsheuser, T. , Franklin, M. T. , Daane, K. M. , Lee, J. C. , Lue, C.‐H. , Girod, P. , Carrillo, J. , Wong, W. H. L. , Kula, R. R. , Gates, M. W. , Hogg, B. N. , Moffat, C. E. , Hoelmer, K. A. , Sial, A. A. , & Buffington, M. L. (2022). A coordinated sampling and identification methodology for larval parasitoids of spotted‐wing Drosophila . Journal of Economic Entomology, 115, 922–942. 10.1093/jee/toab237 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allemand, R. , Fleury, F. , Lemaitre, C. , & Boulétreau, M. (1999). Dynamique des populations et interactions compétitives chez deux espèces de Leptopilina, parasitoïdes, dans la vallée du Rhône (Hymenoptera: Figitidae). Annales de la Société entomologique de France, 35, 97–103.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

