Quanduzhong capsules for the treatment of grade 1 hypertension patients with low-to-moderate risk: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 36703729
- PMCID: PMC9871381
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1014410
Quanduzhong capsules for the treatment of grade 1 hypertension patients with low-to-moderate risk: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Abstract
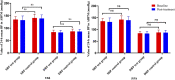
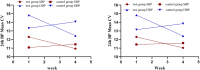
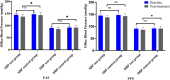
Background: Duzhong [DZ (Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.)] is regarded as a traditional Chinese medicine with a history dating back more than 2000 years. This herb is considered a nourishing herb in China and is commonly used as a tonic to strengthen muscles and bones, nourish the kidneys and liver, and soothe miscarriages. Moreover, there is evidence that DZ is capable of regulating blood pressure (BP), and several compounds isolated from DZ have been shown to have a BP-lowering effect. Quanduzhong capsules contain an extract of DZ [Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. (Eucommiaceae; Eucommiae cortex)] that is effective in treating hypertension. This multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial sought to evaluate the clinical efficacy of Quanduzhong capsules in the treatment of low-to-moderate risk grade 1 hypertension patients. Materials and methods: A total of 60 patients from 3 centers with documented low-to-moderate risk grade 1 hypertension were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to the test group or the control group. After a 1 week lead-in period using sham Quanduzhong capsules, all patients who met the entry criteria (29 cases in the test group and 29 cases in the control group) entered the 4 week test period. The test group took Quanduzhong capsules, and the control group continued to take sham Quanduzhong capsules. The primary endpoints [24-h mean systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) determined via 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM); office SBP and DBP] and secondary endpoints [mean arterial pressure; mean pulse; daytime mean SBP and DBP; nocturnal mean SBP and DBP; SBP and DBP load; area under the blood pressure (BP) curve; morning peak BP; early morning SBP and DBP; smoothness index of SBP and DBP; 24 h BP mean coefficient of variation (CV); percentage of patients with circadian restoration in ABPM; home BP; quality of life evaluated by WHO Quality of Life-BREF questionnaire; grading and quantitative evaluation of hypertension symptoms; values of plasmatic renin activity, angiotensin II, aldosterone, β-2 microglobulin and homocysteine] were assessed following the treatment. Drug-related adverse events and adverse drug reactions were also compared. Results: After a 4 week test period, a significant difference in the DBP CV between the two groups was observed (-2.49 ± 4.32 vs. 0.76 ± 4.3; p < .05). Moreover, the mean office SBP change was -7.62 ± 9.32 mmHg, and the mean DBP change was -4.66 ± 6.03 (p < .05). Among the three subjects with abnormal homocysteine levels in the test group, homocysteine levels decreased by 6.23 ± 9.15 μmol/L after treatment. No differences were observed between the two groups in any other indicators. After 4 weeks of treatment, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of safety indicators (p > .05). No abnormal vital signs (except BP) or severe liver or renal function impairment were observed during the treatment periods; in addition, adverse events and drug reactions were mild. Conclusion: Treatment with Quanduzhong capsules reduced office SBP and DBP as well as DBP CV determined by 24-h ambulatory BP monitoring in patients with grade 1 hypertension at low-to-moderate risk. Clinical Trial Registration: https://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=32531, identifier ChiCTR1900021699.
Keywords: grade 1 hypertension; low-to-moderate risk; quanduzhong capsule; randomized controlled trial; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Tian, Duan, Pan, Huang, Wang, Yang, Wen, Tang, Xiong, Zhu, Liu, Wei, Qi, Ouyang, Ying, Wang, Zhou, Li, Cui, Yang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
ZZ, XL, YC and SY are employed by Jiangxi Puzheng Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer XX declared a shared parent affiliation with the authors XX, WT, WD and HX to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A multicenter, randomized, double-blind comparison of the efficacy and safety of irbesartan and enalapril in adults with mild to moderate essential hypertension, as assessed by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: the MAPAVEL Study (Monitorización Ambulatoria Presión Arterial APROVEL).Clin Ther. 2002 Jan;24(1):126-38. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(02)85010-x. Clin Ther. 2002. PMID: 11833827 Clinical Trial.
-
A multicenter, 14-week study of telmisartan and ramipril in patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension using ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.Am J Hypertens. 2006 Jan;19(1):104-12. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.10.001. Am J Hypertens. 2006. PMID: 16461201 Clinical Trial.
-
[A Brazilian multicenter study to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and tolerance of isradipine SRO using ambulatory monitoring of arterial pressure in the treatment of mild and moderate arterial hypertension].Arq Bras Cardiol. 1993 Nov;61(5):311-8. Arq Bras Cardiol. 1993. PMID: 8147731 Clinical Trial. Portuguese.
-
Comparing the Effectiveness of Home, Clinic, and Kiosk Blood Pressure Checks for Diagnosing High Blood Pressure – The BP-CHECK Study [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 Aug. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 Aug. PMID: 39078929 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of azilsartan medoxomil in the treatment of hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 4;11:1383217. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1383217. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39026999 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extraction and Purification of Aucubin from Eucommia ulmoides Seed Draff in Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Macroporous Resins.ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 29;9(1):1723-1737. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08332. eCollection 2024 Jan 9. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38222590 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Correlation Between Hypertension and Gut Microbiota.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 May 16;17:2371-2387. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S463880. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38770171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of a Deep Eutectic Solvent and Macroporous Resin for Green Recovery of Iridoids, Chlorogenic Acid, and Flavonoids from Eucommia ulmoides Leaves.Molecules. 2024 Feb 5;29(3):737. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030737. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338480 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical properties, biological activities, applications, and protective potential of the skeletal system of Eucommia ulmoides polysaccharides: a review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 13;16:1570095. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1570095. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40183083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The clinical effects of continuous nursing intervention combined with chronic disease management center in patients with severe hypertension.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jan 10;104(2):e40819. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040819. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39792737 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Belknap R., Holland D., Feng P. J., Millet J. P., Caylà J. A., Martinson N. A., et al. TB Trials Consortium iAdhere Study Team (2017). Self-administered versus directly observed once-weekly isoniazid and rifapentine treatment of latent tuberculosis infection: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern Med. 167 (10), 689–697. 10.7326/M17-1150 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cronquist A. (1981). An integrated system of classification of flowering plants. New York: Columbia University Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

