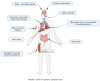
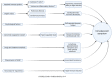
The pathological mechanism of the COVID-19 convalescence and its treatment with traditional Chinese medicine
- PMID: 36703736
- PMCID: PMC9872123
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1054312
The pathological mechanism of the COVID-19 convalescence and its treatment with traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus - 2 (SARS - CoV - 2) was reported to cause the Wuhan outbreak of the corona virus disease 2019(COVID-19). To date, the COVID-19 has infected more than 600 million people gloabally. As a growing number of patients recover from acute infections and are discharged from hospitals, the proportion of patients in the recovery period is gradually increasing. Many of these individuals have been reported to experience multiple symptoms during the convalescence, such as fatigue, dyspnea and pain which are designated as "long-COVID", "post-COVID syndrome" or "recovery sequelae. We searched for recent articles published in PubMed on COVID-19 convalescence and found that the pathogenesis of COVID-19 convalescence is not yet well recognized. It may be associated with incomplete recovery of immune system, parenchymal organ damage (liver or lung), coagulation abnormalities, "second hit" caused by viral infection, and Phenomenon of Cell Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP). Some drugs and psychological factors of patients also play a non-negligible role in it. We also found that the effect of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is effective in the treatment of the COVID-19 recovery phase, which can not only relieve the corresponding symptoms, but also improve the indicators and pulmonary fibrosis. Bufei Huoxue Capsule, as the only drug explicitly mentioned for COVID-19 recovery period, can exert strong rehabilitative effects on physiological activity in patients recovering from COVID-19. In addition, in previous studies, traditional Chinese medicine has been confirmed to have the ability to resist cytokine storms, as well as improve coagulation and myocardial damage, which makes it have potential therapeutic advantages in targeting the hyperimmune response, coagulation abnormalities and myocardial damage existing in the recovery period. In conclusion, the clinical symptoms of patients convalescing from COVID-19 are complex, and its pathogenesis has not been elucidated. traditional Chinese medicine, as a traditional treatment, its specific action and mechanism need to be confirmed by more studies, so that it can play a better role.
Keywords: COVID-19; TCM (trad. Chinese medicine); long-COVID-19; mechanism; recovery period.
Copyright © 2023 Jiang, An, Duan, Lian, Jin, Zhang, Yang, Zhang, Kang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of Bufei Huoxue capsules in the management of convalescent patients with COVID-19 infection: A multicentre, double-blind, and randomised controlled trial.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;284:114830. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114830. Epub 2021 Nov 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34763045 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Maxingshigan-Weijing in the management of COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Dec 23;21(1):1029. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04970-3. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33357239 Free PMC article.
-
[Standard technical specifications for methacholine chloride (Methacholine) bronchial challenge test (2023)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 12;47(2):101-119. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20231019-00247. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38309959 Chinese.
-
The direct evidence and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of COVID-19.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111267. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111267. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33508618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Practice and principle of traditional Chinese medicine for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19.Front Med. 2023 Dec;17(6):1014-1029. doi: 10.1007/s11684-023-1040-8. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 38157191 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical effects of traditional Chinese herbal medicine management in patients with COVID-19 sequelae: A hospital-based retrospective cohort study in Taiwan.Int J Med Sci. 2024 May 13;21(7):1280-1291. doi: 10.7150/ijms.96575. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38818462 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicines for long COVID: A phase 2 pilot clinical study.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 13;10(18):e37920. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37920. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39328557 Free PMC article.
-
Explainable machine learning model and nomogram for predicting the efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine in treating Long COVID: a retrospective study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 13;12:1529993. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1529993. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40182854 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for post-COVID: A retrospective cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 2;104(18):e42275. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042275. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40327434 Free PMC article.
-
Precision nutrition to reset virus-induced human metabolic reprogramming and dysregulation (HMRD) in long-COVID.NPJ Sci Food. 2024 Mar 30;8(1):19. doi: 10.1038/s41538-024-00261-2. NPJ Sci Food. 2024. PMID: 38555403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous