The efficacy of ginseng-containing traditional Chinese medicine in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36703755
- PMCID: PMC9871309
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1083001
The efficacy of ginseng-containing traditional Chinese medicine in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of ginseng-containing traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). Methods: Seven databases were included from establishment until 10 July 2022. Pooled data were analyzed with random-effects model. The risk of bias was measured by the risk of bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2). Modified Jadad scale score was used to assess the quality of including studies. The meta-analysis was performed with RevMan 5.3. Trial sequential analysis was assessed to avoid type I errors. We have registered our protocol in PROSPERO (CRD42021267742). Results: Twenty-eight articles were included. The results demonstrated that compared with conventional western therapy (WT), ginseng-containing TCM combined with WT further improved clinical efficacy (RR: 1.25, 95% CI: 1.20-1.29, p < 0.00001, I2 = 8%), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (MD: 5.80, 95% CI: 4.86-6.74, p < 0.00001, I2 = 89%), stroke volume (MD: 13.80, 95% CI: 12.66-14.95, p < 0.00001, I2 = 93%), 6-min walk test (MD: 53.03, 95% CI: 20.76-85.29, p = 0.001, I2 = 97%), decreased 6-month rehospitalization (RR: 0.44, 95% CI: 0.18-1.11, p = 0.08, I2 = 0%), brain natriuretic peptide (MD: 188.12, 95% CI: 248.13 to -128.11, p < 0.00001, I2 = 94%), N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (MD = -503.29; 95% CI: 753.18 to -253.40, p < 0.0001, I2 = 89%) and Minnesota living heart failure questionnaire scores (MD: 9.68, 95% CI: 13.67 to -5.70, p < 0.00001, I2 = 83%). The ROB2 assessment and modified Jaded scores showed most studies included were with some concerns. Conclusion: Compared with WT alone, ginseng-containing TCM is a possible way to benefit ADHF patients. However, limited by the quality of including trials, more high-quality studies are needed to provide reliable evidence.
Keywords: acute decompensated heart failure; adverse reactions and cases; ginseng-containing traditional Chinese medicine; heart function; left ventricular ejection fraction; quality of life.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Ma, Li, Yao, Gui, Lu, Zhou, Wang and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
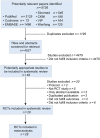
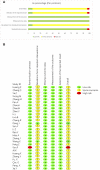
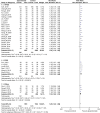

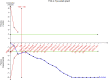

Comment in
-
Commentary: The efficacy of ginseng-containing traditional Chinese medicine in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 1;14:1180944. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1180944. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37593180 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The efficacy of Yiqi Huoxue therapy for chronic heart failure: A meta-analysis in accordance with PRISMA guideline.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Aug 26;101(34):e30082. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030082. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36042620 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine Cutaneous Regions Therapy as adjuvant treatment of chronic heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2023 May 2;9(5):e16012. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16012. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37206004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Chinese Herbal Medicine for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Meta-Analysis.Chin J Integr Med. 2019 Oct;25(10):770-777. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-2704-8. Epub 2019 May 24. Chin J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31127505
-
Effect of pueraria on left ventricular remodelling in HFrEF: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 4;18(12):e0295344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295344. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38048301 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of astragalus injection on left ventricular remodeling in HFmrEF: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Aug 6;11:1374114. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1374114. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39165261 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ginseng supplementation and vascular function: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jul 11;25(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04936-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40646515 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary: The efficacy of ginseng-containing traditional Chinese medicine in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 1;14:1180944. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1180944. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37593180 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inhibition of Myocardial Remodeling and Heart Failure by Traditional Herbal Medications: Evidence from Ginseng and ginkgo biloba.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jul 21;24(7):212. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2407212. eCollection 2023 Jul. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39077021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms and intervention approaches of heart failure (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Aug;56(2):125. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5566. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40511535 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ai K., Xu L. (2019). Clinical effect of Qiliqiangxin capsule in treatment of patients with acute attack of chronic heart failure. Clin. Res. Pract. 4, 136–138.
-
- An L., Zhang X., Huang W., Wang L., Li M. (2017). Effectiveness of combining recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide with injectable Yiqi Fumai in the treatment of ADHF in elderly people with coronary artery disease. Med. Innov. China 14, 85–88.
-
- Chan K. K. L., Yao T. J., Jones B., Zhao J. F., Ma F. K., Leung C. Y., et al. (2011). The use of Chinese herbal medicine to improve quality of life in women undergoing chemotherapy for ovarian cancer: A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial with immunological monitoring. Ann. Oncol. 22, 2241–2249. 10.1093/annonc/mdq749 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

