Investigation of drug-related problems in patients hospitalized in chest disease wards: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 36703759
- PMCID: PMC9872030
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1049289
Investigation of drug-related problems in patients hospitalized in chest disease wards: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
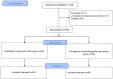
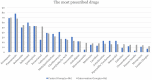
Objective: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), chest diseases are among the 10 diseases that cause the highest mortality worldwide. Drug-related problems (DRPs), readmission, and antimicrobial resistance are critical problems in chest disease wards. Active involvement of clinical pharmacists (CPs) who are focused on reducing the risks of potential problems is needed. The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of pharmaceutical care (PC) services on the pulmonology service. Method: A randomized controlled trial at a university hospital in Istanbul was conducted between June 2020 and December 2021. The participants were randomized into the control group (CG) and intervention group (IG). In the CG, CPs identified and classified the DRPs according to Pharmaceutical Care Network Europe v9.0 (PCNE) and provided solutions to DRPs for the IG. The effect of PC services was evaluated by the number and classification of DRPs, and readmissions within 30 days were compared between the two groups. Results: Out of 168 patients, 82 were assigned to the IG. The average number of medicines administered per patient in the CG and IG was 14.45 ± 7.59 and 15.5 ± 6.18, respectively. In the CG and IG, the numbers of patients with DRPs were 62 and 46, respectively. The total number of DRPs was 160 for CG and 76 for IG. A statistically significant difference was found in favor of the IG, in terms of the number of patients with DRPs, the total number of DRPs, and readmission within 30 days (p < 0.05). Conclusion: In this study, CP recommendations were highly accepted by the healthcare team. Pharmaceutical care services provided by CPs would decrease possible DRPs and led to positive therapeutic outcomes. Cognitive clinical pharmacy services have beneficial effects on health care, and these services should be expanded in all settings where patients and pharmacists are present.
Keywords: chest diseases; clinical pharmacist; cognitive pharmacy services; drug-related problems; pharmaceutical care.
Copyright © 2023 Bektay, Sancar, Okyaltirik, Durdu and Izzettin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the Effect of Management of Drug-Related Problems on Clinical Outcomes of Pulmonary Embolism Outpatients: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 12;14(4):1202. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041202. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004736 Free PMC article.
-
Handling drug-related problems in rehabilitation patients: a randomized study.Int J Clin Pharm. 2012 Apr;34(2):382-8. doi: 10.1007/s11096-012-9623-5. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Int J Clin Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22388601 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the clinical pharmacist's effect on achieving treatment goals in patients with hypothyroidism: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Apr 8;25(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01914-3. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40200273 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Can clinical pharmacy services have a positive impact on drug-related problems and health outcomes in community-based older adults?Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2004 Mar;2(1):3-13. doi: 10.1016/s1543-5946(04)90002-5. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15555474 Review.
-
Evaluation of Pharmacist Medication Review Service in an Outpatient Heart Failure Clinic.J Pharm Pract. 2020 Dec;33(6):820-826. doi: 10.1177/0897190019842696. Epub 2019 May 5. J Pharm Pract. 2020. PMID: 31057060 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacy practice and policy research in Türkiye: a systematic review of literature.J Pharm Policy Pract. 2024 Aug 12;17(1):2385939. doi: 10.1080/20523211.2024.2385939. eCollection 2024. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2024. PMID: 39139388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and evaluation of drug-related problems in community pharmacy in Turkey: a descriptive prevalence study.BMC Prim Care. 2025 Aug 7;26(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12875-025-02926-7. BMC Prim Care. 2025. PMID: 40775745 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacists's knowledge, attitude, and practices towards pharmaceutical and patient-centred care in asthma management: A national study.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Aug;32(8):102140. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102140. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 39109163 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effect of Management of Drug-Related Problems on Clinical Outcomes of Pulmonary Embolism Outpatients: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 12;14(4):1202. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041202. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayhan Y. E., Karakurt S., Sancar M. (2022). The effect of the clinical pharmacist in minimizing drug-related problems and related costs in the intensive care unit in Turkey: A non-randomized controlled study. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 47 (11), 1867–1874. - PubMed
-
- Bekele F., Fekadu G., Bekele K., Dugassa D., Sori J. (2021). Drug-related problems among patients with infectious disease admitted to medical wards of Wollega University Referral Hospital: Prospective observational study. SAGE Open Med. 9, 2050312121989625. 10.1177/2050312121989625 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bethesda (2012). LiverTox: Clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury. Internet Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31643179/ . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous