An occupational health survey on health utility and occupational diseases in Chinese university staff to inform cost-utility analysis
- PMID: 36703839
- PMCID: PMC9871467
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1022344
An occupational health survey on health utility and occupational diseases in Chinese university staff to inform cost-utility analysis
Abstract
Background: The occupational health of university staff bears great social and economic value for which health utility is an indivisible aspect. Utility is also the primary data for the cost-utility analysis of occupational health programs. Health utility and occupational diseases have not been reported for the university staff in China. In the light of "Healthy China," we conducted this study aiming to (1) estimate the health utility of university staff to inform cost-utility analysis and (2) screen and identify potential occupational diseases for this occupation and examine their impacts on health.
Methods: An occupational health survey was conducted in a sample of working-age university staff. Participants were interviewed face-to-face using the WHO Health and Work Performance Questionnaire and the European Quality of Life 5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) instrument to measure health conditions and health utility, respectively. The univariate analysis included the t-test, chi-square test, and correlation techniques. Multivariate generalized linear models were applied to evaluate the significance of each health condition when controlling for other factors.
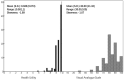
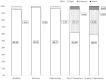
Results: The sample (n = 154) had a mean age of 40.65 years and consisted of slightly more women (51.30%). Participants attained a mean (standard deviation) health utility of 0.945 (0.073). The most affected domain was anxiety/depression with 62 (40.26%) participants reporting problems, followed by pain/discomfort which captured 60 (37.66%) staff with problems. Thus, pain and psychologically related conditions were prevalent. Multivariate models identified two conditions that can significantly reduce the health utility. The psychological/emotional conditions were associated with a utility loss of -0.067 (95%CI: -0.089, -0.045). The pain in body parts other than the head, neck, and back reduced the utility by -0.034 (95%CI: -0.055, -0.014).
Conclusion: Working-age staff in Chinese universities may have a lower health utility than the general population. Psychological conditions and musculoskeletal pain appear like occupational diseases. With the health utility data available, economic evaluation of cost-utility should follow up to facilitate the implementation of cost-effective programs.
Keywords: EQ-5D-5L = EuroQol 5-dimensions 5-level; health related quality of life; health utility; occupational health; real-world evidence (RWE); university staff.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Zhou, Wei, Li, Luo, Naidoo, Zhang, Bi and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential Psychometric Properties of EuroQoL 5-Dimension 5-Level and Short-Form 6-Dimension Utility Measures in Low Back Pain.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019 Jun 1;44(11):E679-E686. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002939. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019. PMID: 30475342
-
Health-related quality of life measured using the EQ-5D-5L: South Australian population norms.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2016 Sep 20;14(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12955-016-0537-0. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2016. PMID: 27644755 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life of patients with HIV/AIDS at a tertiary care teaching hospital in Ethiopia.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021 Jan 19;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01670-7. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021. PMID: 33468153 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid modelling approach for eliciting health state preferences: the Portuguese EQ-5D-5L value set.Qual Life Res. 2019 Dec;28(12):3163-3175. doi: 10.1007/s11136-019-02226-5. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Qual Life Res. 2019. PMID: 31201730
-
Health-related quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of EuroQoL (EQ-5D) utility scores from Asia.Int J Rheum Dis. 2021 Mar;24(3):314-326. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14066. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 33486900
Cited by
-
A Pilot Study on Improving Patient Satisfaction in Kazakhstan: A Service Design Approach.Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2025 May 8;30(3):391-396. doi: 10.4103/ijnmr.ijnmr_362_23. eCollection 2025 May-Jun. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2025. PMID: 40520404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen N, Li X, Liu Q, Liu Y. Systematic review of university teachers' mental health based on SCL-90. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. (2014) 43:990–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical