Hypoxia signaling in cancer: Implications for therapeutic interventions
- PMID: 36703877
- PMCID: PMC9870816
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.203
Hypoxia signaling in cancer: Implications for therapeutic interventions
Abstract
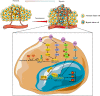
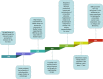
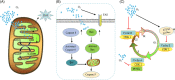
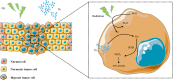
Hypoxia is a persistent physiological feature of many different solid tumors and a key driver of malignancy, and in recent years, it has been recognized as an important target for cancer therapy. Hypoxia occurs in the majority of solid tumors due to a poor vascular oxygen supply that is not sufficient to meet the needs of rapidly proliferating cancer cells. A hypoxic tumor microenvironment (TME) can reduce the effectiveness of other tumor therapies, such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. In this review, we discuss the critical role of hypoxia in tumor development, including tumor metabolism, tumor immunity, and tumor angiogenesis. The treatment methods for hypoxic TME are summarized, including hypoxia-targeted therapy and improving oxygenation by alleviating tumor hypoxia itself. Hyperoxia therapy can be used to improve tissue oxygen partial pressure and relieve tumor hypoxia. We focus on the underlying mechanisms of hyperoxia and their impact on current cancer therapies and discuss the prospects of hyperoxia therapy in cancer treatment.
Keywords: hyperoxia; hypoxia‐inducible factor (HIF); immunotherapy; targeted theraphy; tumor hypoxia.
© 2023 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Solid tumor physiology and hypoxia-induced chemo/radio-resistance: novel strategy for cancer therapy: nitric oxide donor as a therapeutic enhancer.Nitric Oxide. 2008 Sep;19(2):205-16. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2008.04.026. Epub 2008 May 6. Nitric Oxide. 2008. PMID: 18503779 Review.
-
Systemic oxygenation weakens the hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor 1α-dependent and extracellular adenosine-mediated tumor protection.J Mol Med (Berl). 2014 Dec;92(12):1283-92. doi: 10.1007/s00109-014-1189-3. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. PMID: 25120128 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-modulatory nanomaterials to relieve tumor hypoxic microenvironment and enhance immunotherapy: Where do we stand?Acta Biomater. 2021 Apr 15;125:1-28. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.02.030. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33639310 Review.
-
In vivo hyperoxia induces hypoxia-inducible factor-1α overexpression in LNCaP tumors without affecting the tumor growth rate.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;51:65-74. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.03.019. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24704415
-
The hypoxia-driven crosstalk between tumor and tumor-associated macrophages: mechanisms and clinical treatment strategies.Mol Cancer. 2022 Sep 8;21(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01645-2. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36071472 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxic Effects on Matrix Metalloproteinases' Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment and Therapeutic Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 28;24(23):16887. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316887. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modifications of Nanobubble Therapy for Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 2;25(13):7292. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137292. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiopharmaceuticals: navigating the frontier of precision medicine and therapeutic innovation.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 5;29(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01627-0. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38183131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-activated ADCC-enhanced humanized anti-CD147 antibody for liver cancer imaging and targeted therapy with improved selectivity.MedComm (2020). 2024 Mar 11;5(3):e512. doi: 10.1002/mco2.512. eCollection 2024 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38469549 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyocytes in Hypoxia: Cellular Responses and Implications for Cell-Based Cardiac Regenerative Therapies.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;12(2):154. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12020154. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mills DB, Boyle RA, Daines SJ, et al. Eukaryogenesis and oxygen in Earth history. Nat Ecol Evol. 2022;6(5):520‐532. - PubMed
-
- Harris AL. Hypoxia–a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(1):38‐47. - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Ye JJ, Xia Y, et al. Platelet‐Mimicking biotaxis targeting vasculature‐disrupted tumors for cascade amplification of hypoxia‐sensitive therapy. ACS Nano. 2019;13(12):14230‐14240. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
