Calpain-2 Facilitates Autophagic/Lysosomal Defects and Apoptosis in ARPE-19 Cells and Rats Induced by Exosomes from RPE Cells under NaIO3 Stimulation
- PMID: 36703913
- PMCID: PMC9873447
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/3310621
Calpain-2 Facilitates Autophagic/Lysosomal Defects and Apoptosis in ARPE-19 Cells and Rats Induced by Exosomes from RPE Cells under NaIO3 Stimulation
Abstract
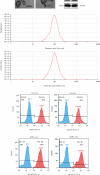
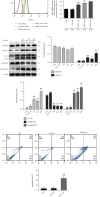
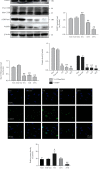
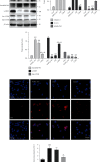
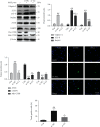
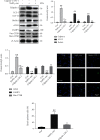
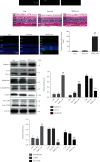
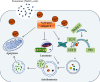
Although accumulated evidence supports the notion that calpain contributes to eye disease, the mechanisms by which calpain promotes RPE injury are not defined. The present study is aimed at investigating whether the effect of NaIO3-exos (exosomes derived from RPE cells under NaIO3 stimulation) on the dysfunction of the autophagy-lysosomal pathway (ALP) and apoptosis is based on its regulation of calpain activation in ARPE-19 cells and rats. The results showed that calpain-2 activation, ALP dysfunction, and apoptosis were induced by NaIO3-exos in ARPE-19 cells. NaIO3-exo significantly increased autophagic substrates by activating lysosomal dysfunction. ALP dysfunction and apoptosis in vitro could be eliminated by knocking down calpain-2 (si-C2) or the inhibitor calpain-2-IN-1. Further studies indicated that NaIO3-exo enhanced calpain-2 expression, ALP dysfunction, apoptosis, and retinal damage in rats. In summary, these results demonstrate for the first time that calpain-2 is one of the key players in the NaIO3-exo-mediated ALP dysfunction, apoptosis, and retinal damage and identify calpain-2 as a promising target for therapies aimed at age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Copyright © 2023 Shuaishuai Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium Iodate Disrupted the Mitochondrial-Lysosomal Axis in Cultured Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Sep;34(7):500-511. doi: 10.1089/jop.2017.0073. Epub 2018 Jul 18. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30020815
-
Reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy confer protective effects in retinal pigment epithelial cells against sodium iodate-induced cell death.J Biomed Sci. 2019 May 22;26(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0531-z. J Biomed Sci. 2019. PMID: 31118030 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress-Induced Pentraxin 3 Expression Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 29;20(23):6028. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236028. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31795454 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomes: Regulators of autophagy in the retinal pigmented epithelium.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Mar;144:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.08.018. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26321509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defects in retinal pigment epithelial cell proteolysis and the pathology associated with age-related macular degeneration.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016 Mar;51:69-89. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26344735 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Extracellular-Vesicles-Based Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches for Ocular Diseases.ACS Nano. 2024 Aug 27;18(34):22793-22828. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c08486. Epub 2024 Aug 14. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39141830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal ions overloading and cell death.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Aug 20;40(1):72. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09910-4. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39162885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Choroidal Mast Cells and Pathophysiology of Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Cells. 2023 Dec 26;13(1):50. doi: 10.3390/cells13010050. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38201254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances of exosomes in age-related macular degeneration.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 2;14:1204351. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1204351. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37332352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

