Effect of static magnetic field on marine mollusc Elysia leucolegnote
- PMID: 36703918
- PMCID: PMC9871387
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1103648
Effect of static magnetic field on marine mollusc Elysia leucolegnote
Abstract
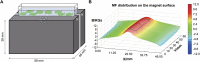
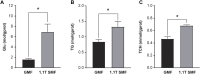
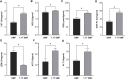
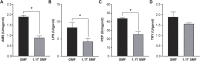
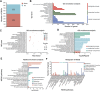
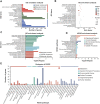
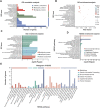
Artificial magnetic fields are unavoidable environment for offshore marine organisms. With the substantially increasing submarine cables, the impact of magnetic field generated by cables on marine organisms has gradually attracted people's attention. However, there are few studies on the effect of magnetic field on molluscs. To explore whether magnetic fields could interfere with the physiological functions of offshore molluscs, here we systematically analyzed the change of metabolism and transcriptome of Elysia leucolegnote exposed to either geomagnetic field or 1.1 T static magnetic field. The blood glucose and lipid levels, as well as the activities of antioxidant enzymes in E. leucolegnote were significantly increased upon the exposure to high static magnetic field for 10 days. Meanwhile, the activities of enzymes related to digestive performance and liver functions were decreased. Possible mechanisms were further revealed through comparative transcriptome analysis. A total of 836 differentially expressed genes were identified, 352 of which were up-regulated and 484 of which were down-regulated after exposure to the high static magnetic field. The up-regulated differential genes were mainly concentrated in lysosomal and apoptotic pathways, and down-regulated differential genes were mainly involved in digestive and immune systems including phagocytosis. This pattern was further confirmed by RT-qPCR analysis. In conclusion, prolonged exposure to a 1.1 T static magnetic field increased oxidative stress and blood glucose and lipid levels, and decreased immunity and physiological conditions in E. leucolegnote. The data we presented here provides a comprehensive view of metabolism change and gene expression pattern of E. leucolegnote exposed to static magnetic field. It may expand our knowledge on the magnetic field effects on offshore mollusc at molecular level, and contribute to clarification of the interaction between marine animals and artificial magnetic fields, which is certainly ecologically important.
Keywords: Elysia leucolegnote; apoptosis; digestive; geomagnetic field; oxidative stress; static magnetic field; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2023 Fei, Zhang, Li, Wang, Feng, Wan and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Do magnetic fields related to submarine power cables affect the functioning of a common bivalve?Mar Environ Res. 2022 Jul;179:105700. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2022.105700. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Mar Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35841831
-
Exploring the impact of magnetic fields related to submarine power cables on the American mud crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii: A behavioural and physiological perspective.Mar Pollut Bull. 2025 Mar;212:117492. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.117492. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Mar Pollut Bull. 2025. PMID: 39729833
-
Introducing energy into marine environments: A lab-scale static magnetic field submarine cable simulation and its effects on sperm and larval development on a reef forming serpulid.Environ Pollut. 2023 Jul 1;328:121625. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121625. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Environ Pollut. 2023. PMID: 37085101
-
Offshore windmills and the effects of electromagnetic fields on fish.Ambio. 2007 Dec;36(8):630-3. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[630:owateo]2.0.co;2. Ambio. 2007. PMID: 18240676 Review.
-
Potential interactions between diadromous fishes of U.K. conservation importance and the electromagnetic fields and subsea noise from marine renewable energy developments.J Fish Biol. 2012 Jul;81(2):664-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.2012.03374.x. J Fish Biol. 2012. PMID: 22803729 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Electromagnetic Fields in Cellular Interactions and Cacao Bean Fermentation.Foods. 2024 Sep 26;13(19):3058. doi: 10.3390/foods13193058. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39410093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrokinetic properties of healthy and β-thalassemia erythrocyte membranes under in vitro exposure to static magnetic field.Front Chem. 2023 Oct 19;11:1197210. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1197210. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37927566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alken P., Thébault E., Beggan C. D., Amit H., Aubert J., Baerenzung J., et al. (2021). International geomagnetic reference field: The thirteenth generation. Earth, Planets Space 73 (1), 49. 10.1186/s40623-020-01288-x - DOI
-
- Bearoff F., Fuller-Espie S. L. (2011). Alteration of mitochondrial membrane potential (∆Ψm) and phosphatidylserine translocation as early indicators of heavy metal-induced apoptosis in the earthworm Eisenia hortensis . ISJ-Invertebrate Surviv. J. 8, 98–108.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

