Modeling sepsis, with a special focus on large animal models of porcine peritonitis and bacteremia
- PMID: 36703923
- PMCID: PMC9871395
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1094199
Modeling sepsis, with a special focus on large animal models of porcine peritonitis and bacteremia
Abstract
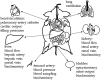
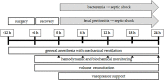
Infectious diseases, which often result in deadly sepsis or septic shock, represent a major global health problem. For understanding the pathophysiology of sepsis and developing new treatment strategies, reliable and clinically relevant animal models of the disease are necessary. In this review, two large animal (porcine) models of sepsis induced by either peritonitis or bacteremia are introduced and their strong and weak points are discussed in the context of clinical relevance and other animal models of sepsis, with a special focus on cardiovascular and immune systems, experimental design, and monitoring. Especially for testing new therapeutic strategies, the large animal (porcine) models represent a more clinically relevant alternative to small animal models, and the findings obtained in small animal (transgenic) models should be verified in these clinically relevant large animal models before translation to the clinical level.
Keywords: SOFA score; bacteremia; cardiovascular system; immune system; large animal models; peritonitis; pig; sepsis.
Copyright © 2023 Vintrych, Al-Obeidallah, Horák, Chvojka, Valešová, Nalos, Jarkovská, Matějovič and Štengl.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SOFA Score, Hemodynamics and Body Temperature Allow Early Discrimination between Porcine Peritonitis-Induced Sepsis and Peritonitis-Induced Septic Shock.J Pers Med. 2021 Feb 28;11(3):164. doi: 10.3390/jpm11030164. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33670874 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental models of sepsis and their clinical relevance.Shock. 2008 Oct;30 Suppl 1:53-9. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318181a343. Shock. 2008. PMID: 18704008 Review.
-
Characterization of Fecal Peritonitis-Induced Sepsis in a Porcine Model.J Surg Res. 2019 Dec;244:492-501. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.06.094. Epub 2019 Jul 19. J Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31330293
-
A Porcine Sepsis Model With Numerical Scoring for Early Prediction of Severity.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 9;9:867796. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.867796. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35615093 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory models of sepsis and septic shock.J Surg Res. 1990 Aug;49(2):186-96. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(90)90260-9. J Surg Res. 1990. PMID: 2199735 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Hepatic Gene Expression Profiles in Murine and Porcine Sepsis Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 15;25(20):11079. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011079. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456859 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Oxiris® Therapy on Cytokine Elimination after a LPS Infusion-An Experimental Animal Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 27;25(17):9283. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179283. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273234 Free PMC article.
-
A TriAdj-Adjuvanted Chlamydia trachomatis CPAF Protein Vaccine Is Highly Immunogenic in Pigs.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Apr 16;12(4):423. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040423. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675805 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating skeletal muscle wasting and weakness in models of critical illness.Clin Sci (Lond). 2025 Jul 1;139(13):743-67. doi: 10.1042/CS20255458. Clin Sci (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40591724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of the PD9-9 Monoclonal Antibody for Identifying Porcine Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;14(9):1054. doi: 10.3390/life14091054. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Obeidallah M., Jarkovská D., Valešová L., Horák J., Jedlička J., Nalos L., et al. (2021). SOFA score, hemodynamics and body temperature allow early discrimination between porcine peritonitis-induced sepsis and peritonitis-induced septic shock. J. Pers. Med. 11, 164. 10.3390/jpm11030164 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basas J., Palau M., Ratia C., Del Pozo J. L., Martín-Gómez M. T., Gomis X., et al. (2018). High-dose daptomycin is effective as an antibiotic lock therapy in a rabbit model of Staphylococcus epidermidis catheter-related infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, 017777-17. 10.1128/AAC.01777-17 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

