DNA methylation change of HIPK3 in Chinese rheumatoid arthritis and its effect on inflammation
- PMID: 36703984
- PMCID: PMC9872787
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1087279
DNA methylation change of HIPK3 in Chinese rheumatoid arthritis and its effect on inflammation
Abstract
Introduction: Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 (HIPK3) plays an important role in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation. Over-expression of HIPK3 in immune cells in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been reported. In this study, we investigated blood methylation levels and clinical characteristics of RA in a Chinese population.
Methods: A total of 235 patients with RA, 30 with osteoarthritis (OA), and 30 matched healthy controls were recruited. The methylation status of seven CpGs in the differentially methylated region of HIPK3 (cg05501357) was measured using targeted methylation-sequencing technology. The association between methylation haplotypes and the overall methylation status of HIPK3 with clinical characteristics was assessed using generalized linear regression.
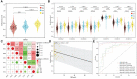
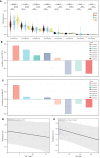
Results: All seven CpGs showed hypomethylation status in RA blood compared with OA and normal individuals (overall p= 1.143×10-8 and FDR= 2.799×10-7), which is consistent with the previously reported high expression of HIPK3 in RA immune cells. Among all seven CpGs, 33286785 showed the highest predictive power with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.829; we received a higher AUC=0.864 when we combined HIPK3 with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA -) and rheumatoid factor (RF +) in the prediction model, indicating that when a patient's ACPA is negative, HIPK3 can assist RF as a new clinical index for the diagnosis of RA. We also found that HIPK3 methylation levels were negatively correlated with C-reactive protein (CRP; r= -0.16, p= 0.01). Methylation haplotypes were analyzed, and the full methylation haplotype (FMH; r= 0.16, p= 0.01) and full non-methylation haplotype (FNH; r= 0.18, p= 0.0061) were negatively correlated with CRP.
Conclusion: Circulating blood methylation levels in the protein region of HIPK3 can be utilized as a supportive diagnostic biomarker and CRP level indicator for RA.
Keywords: DNA methylation; HIPK3; inflammation; methylation haplotypes; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2023 Jiang, Wei, Xu, Chang, Zhang, Zhao, Jin, Xu, Shi, Qian, Sun, Guo, Wang, Qin and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIPK3 hypomethylation as a potential epigenetic biomarker in rheumatic immune diseases with emphasis on rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):115-123. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07158-1. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39602044
-
Circulating DNA methylation level of CXCR5 correlates with inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Jun;11(6):e902. doi: 10.1002/iid3.902. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37382265 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating methylation level of HTR2A is associated with inflammation and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 6;13:1054451. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1054451. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36561742 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of clinical characteristics biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis through targeted DNA methylation sequencing.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Apr 20;131:111860. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111860. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38508093
-
Rheumatoid arthritis-relevant DNA methylation changes identified in ACPA-positive asymptomatic individuals using methylome capture sequencing.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Jul 31;11(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0699-9. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31366403 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
N-Dimethyl chalcone facilitated augmentation of IL-10 and diminution of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, NFκB, and COX-2 in FCA-induced arthritic rat model.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jun;33(6):3119-3134. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01732-y. Epub 2025 Apr 12. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40220200
-
DNA and RNA Methylation in Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Narrative Review.Epigenomes. 2025 Jan 8;9(1):2. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes9010002. Epigenomes. 2025. PMID: 39846569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation analysis of circulating PCDH17 DNA methylation changes with rheumatoid arthritis patients.Sci Rep. 2025 May 23;15(1):17939. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02236-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40410297 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation haplotypes of the insulin gene promoter in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Can a dimensionality reduction approach predict the disease?Exp Ther Med. 2023 Aug 8;26(4):461. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12160. eCollection 2023 Oct. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37664671 Free PMC article.
-
HIPK3 hypomethylation as a potential epigenetic biomarker in rheumatic immune diseases with emphasis on rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):115-123. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07158-1. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39602044
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

