Alpha-1 antitrypsin limits neutrophil extracellular trap disruption of airway epithelial barrier function
- PMID: 36703990
- PMCID: PMC9872031
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1023553
Alpha-1 antitrypsin limits neutrophil extracellular trap disruption of airway epithelial barrier function
Abstract
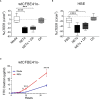
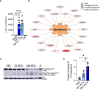
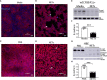
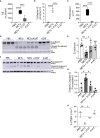
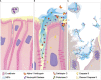
Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to lung injury in cystic fibrosis and asthma, but the mechanisms are poorly understood. We sought to understand the impact of human NETs on barrier function in primary human bronchial epithelial and a human airway epithelial cell line. We demonstrate that NETs disrupt airway epithelial barrier function by decreasing transepithelial electrical resistance and increasing paracellular flux, partially by NET-induced airway cell apoptosis. NETs selectively impact the expression of tight junction genes claudins 4, 8 and 11. Bronchial epithelia exposed to NETs demonstrate visible gaps in E-cadherin staining, a decrease in full-length E-cadherin protein and the appearance of cleaved E-cadherin peptides. Pretreatment of NETs with alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT) inhibits NET serine protease activity, limits E-cadherin cleavage, decreases bronchial cell apoptosis and preserves epithelial integrity. In conclusion, NETs disrupt human airway epithelial barrier function through bronchial cell death and degradation of E-cadherin, which are limited by exogenous A1AT.
Keywords: E-cadherin (CDH1); NETs (neutrophil extracellular traps); alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT); barrier function; bronchial epithelia.
Copyright © 2023 Hudock, Collins, Imbrogno, Kramer, Brewington, Ziady, Zhang, Snowball, Xu, Carey, Horio, O’Grady, Kopras, Meeker, Morgan, Ostmann, Skala, Siefert, Na, Davidson, Gollomp, Mangalmurti, Trapnell and Clancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Young RL, Malcolm KC, Kret JE, Caceres SM, Poch KR, Nichols DP, et al. . Neutrophil extracellular trap (NET)-mediated killing of pseudomonas aeruginosa: evidence of acquired resistance within the CF airway, independent of CFTR. PloS One (2011) 6(9):e23637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023637 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

