EEG Lempel-Ziv complexity varies with sleep stage, but does not seem to track dream experience
- PMID: 36704096
- PMCID: PMC9871639
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.987714
EEG Lempel-Ziv complexity varies with sleep stage, but does not seem to track dream experience
Abstract
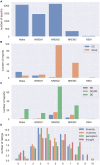
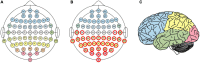
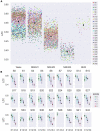
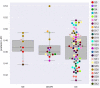
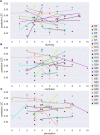
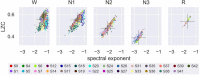
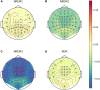
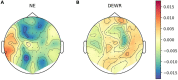
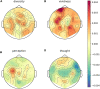
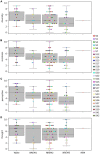
In a recent electroencephalography (EEG) sleep study inspired by complexity theories of consciousness, we found that multi-channel signal diversity progressively decreased from wakefulness to slow wave sleep, but failed to find any significant difference between dreaming and non-dreaming awakenings within the same sleep stage (NREM2). However, we did find that multi-channel Lempel-Ziv complexity (LZC) measured over the posterior cortex increased with more perceptual ratings of NREM2 dream experience along a thought-perceptual axis. In this follow-up study, we re-tested our previous findings, using a slightly different approach. Partial sleep-deprivation was followed by evening sleep experiments, with repeated awakenings and immediate dream reports. Participants reported whether they had been dreaming, and were asked to rate how diverse, vivid, perceptual, and thought-like the contents of their dreams were. High density (64 channel) EEG was recorded throughout the experiment, and mean single-channel LZC was calculated for each 30 s sleep epoch. LZC progressively decreased with depth of non-REM sleep. Surprisingly, estimated marginal mean LZC was slightly higher for NREM1 than for wakefulness, but the difference did not remain significant after adjusting for multiple comparisons. We found no significant difference in LZC between dream and non-dream awakenings, nor any significant relationship between LZC and subjective ratings of dream experience, within the same sleep stage (NREM2). The failure to reproduce our own previous finding of a positive correlation between posterior LZC and more perceptual dream experiences, or to find any other correlation between brain signal complexity and subjective experience within NREM2 sleep, raises the question of whether EEG LZC is really a reliable correlate of richness of experience as such, within the same sleep stage.
Keywords: EEG; complexity; consciousness; dreaming; sleep.
Copyright © 2023 Aamodt, Sevenius Nilsen, Markhus, Kusztor, HasanzadehMoghadam, Kauppi, Thürer, Storm and Juel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EEG Signal Diversity Varies With Sleep Stage and Aspects of Dream Experience.Front Psychol. 2021 Apr 23;12:655884. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.655884. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33967919 Free PMC article.
-
EEG Frontal Alpha Asymmetry and Dream Affect: Alpha Oscillations over the Right Frontal Cortex during REM Sleep and Presleep Wakefulness Predict Anger in REM Sleep Dreams.J Neurosci. 2019 Jun 12;39(24):4775-4784. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2884-18.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 15. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30988168 Free PMC article.
-
Lempel-Ziv complexity of cortical activity during sleep and waking in rats.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Apr 1;113(7):2742-52. doi: 10.1152/jn.00575.2014. Epub 2015 Feb 25. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25717159 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the neuropsychology of dreaming: Insights into the neural basis of dreaming with new techniques of sleep recording and analysis.Sleep Med Rev. 2017 Oct;35:8-20. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Sleep Med Rev. 2017. PMID: 27569701 Review.
-
Complexity Measures for EEG Microstate Sequences: Concepts and Algorithms.Brain Topogr. 2024 Mar;37(2):296-311. doi: 10.1007/s10548-023-01006-2. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Brain Topogr. 2024. PMID: 37751054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sensory modality defines the relation between EEG Lempel-Ziv diversity and meaningfulness of a stimulus.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 1;13(1):3453. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30639-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36859725 Free PMC article.
-
Entropy of difference works similarly to permutation entropy for the assessment of anesthesia and sleep EEG despite the lower computational effort.J Clin Monit Comput. 2025 Aug;39(4):655-668. doi: 10.1007/s10877-024-01258-8. Epub 2024 Dec 26. J Clin Monit Comput. 2025. PMID: 39725813 Free PMC article.
-
The Constrained Disorder Principle May Account for Consciousness.Brain Sci. 2024 Feb 23;14(3):209. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14030209. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38539598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
We are the Sensors of Consciousness! A Review and Analysis on How Awakenings During Sleep Influence Dream Recall.Nat Sci Sleep. 2025 Apr 30;17:709-729. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S506461. eCollection 2025. Nat Sci Sleep. 2025. PMID: 40330584 Free PMC article.
-
Psychedelics and disorders of consciousness: the current landscape and the path forward.Neurosci Conscious. 2024 Jun 15;2024(1):niae025. doi: 10.1093/nc/niae025. eCollection 2024. Neurosci Conscious. 2024. PMID: 38881630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baars B. J. (1988). A cognitive theory of consciousness. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

