Fuzzy-based prediction of solar PV and wind power generation for microgrid modeling using particle swarm optimization
- PMID: 36704286
- PMCID: PMC9871071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12802
Fuzzy-based prediction of solar PV and wind power generation for microgrid modeling using particle swarm optimization
Abstract
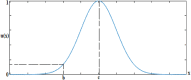
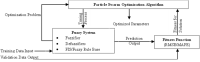
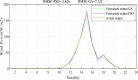
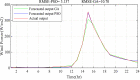
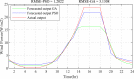
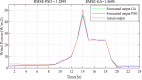
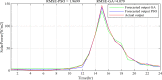
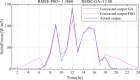
Regardless of their nature of stochasticity and uncertain nature, wind and solar resources are the most abundant energy resources used in the development of microgrid systems. In microgrid systems and distribution networks, the uncertain nature of both solar and wind resources results in power quality and system stability issues. The randomization behavior of solar and wind energy resources is controlled through the precise development of a power prediction model. Fuzzy-based solar PV and wind prediction models may more efficiently manage this randomness and uncertain character. However, this method has several drawbacks, it has limited performance when the volumes of wind and solar resources historical data are huge in size and it has also many membership functions of the fuzzy input and output variables as well as multiple fuzzy rules available. The hybrid Fuzzy-PSO intelligent prediction approach improves the fuzzy system's limitations and hence increases the prediction model's performance. The Fuzzy-PSO hybrid forecast model is developed using MATLAB programming of the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm with the help of the global optimization toolbox. In this paper, an error correction factor (ECF) is considered a new fuzzy input variable. It depends on the validation and forecasted data values of both wind and solar prediction models to improve the accuracy of the prediction model. The impact of ECF is observed in fuzzy, Fuzzy-PSO, and Fuzzy-GA wind and solar PV power forecasting models. The hybrid Fuzzy-PSO prediction model of wind and solar power generation has a high degree of accuracy compared to the Fuzzy and Fuzzy-GA forecasting models. The rest of this paper is organized as: Section II is about the analysis of solar and wind resources row data. The Fuzzy-PSO prediction model problem formulation is covered in Section III. Section IV, is about the results and discussion of the study. Section V contains the conclusion. The references and abbreviations are presented at the end of the paper.
Keywords: ANFIS, Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System; ANN, Artificial Neural Network; ARIMA, Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average; ARMA, Auto-Regressive Moving Average; BPNN, Back Propagation Neural Network; CA, Cultural Algorithm; CNN, Convolutional Neural Network; DNI, Direct Normal Insolation; DSI, Diffused Solar Insolation; ECF, Error Correction Factor; FF, Firefly Algorithm; FOA, Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm; FR, Fuzzy Regression; Fuzzy system; Fuzzy-GA Hybrid algorithm; Fuzzy-PSO Algorithm; GA, Genetic Algorithm; GHI, Global Horizontal Irradiance; LSSVM, Least-Square Support Vector Machine; MAPE, Mean Absolute Percentage Error; NRMSE, Normalized Root-Mean-Square Error; PSO, Particle Swarm Optimization; PV, Photovoltaic; Particle swarm optimization; SVM, Support Vector Machine; SVR, Support Vector Regression; Solar power prediction model; Wind power prediction model.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
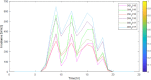
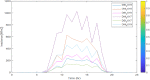
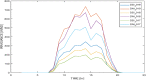
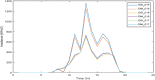
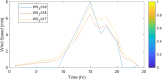
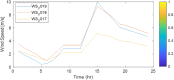
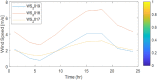
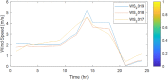
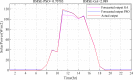
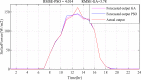
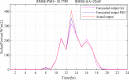
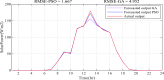
References
-
- Yadav Harendra K., Pal Y., Tripathi Madan Mohan. Annual IEEE India Conference; December 2015. Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Methods in Smart Power Grid; pp. 1–6.
-
- Sun Q., Huang B., Li D., Ma D., Zhang Y. Optimal placement of energy storage devices in microgrids via structure preserving energy function. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. June 2016;12(3):1166–1179.
-
- Li C.D., Wang L., Zhang G.Q., Wang H.D., Shang F. Functional-type single-input-rule-modules connected neural fuzzy system for wind speed prediction. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica. 2017;4(Issue. 4):751–762.
-
- Catalao J.P., Pousinho H.I., Mendes V.F. Hybrid wavelet PSO-ANFIS approach for short term electricity prices forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Sys. February 2010;26(Issue.1) page 137–144.
-
- Khatib T., Mohamed A., Mahmoud M., Sopian K. Modeling of daily solar energy on a horizontal surface for five main sites in Malaysia. Int. J. Green Energy. 2011;8(8):795–819. doi: 10.1080/15435075.2011.602156. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

