Small extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells: A potential Weapon for chronic non-healing wound treatment
- PMID: 36704302
- PMCID: PMC9872203
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1083459
Small extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells: A potential Weapon for chronic non-healing wound treatment
Abstract
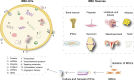
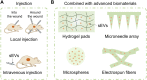
Chronic non-healing wounds have posed a severe threat to patients mentally and physically. Behavior dysregulation of remaining cells at wound sites is recognized as the chief culprit to destroy healing process and hinders wound healing. Therefore, regulating and restoring normal cellular behavior is the core of chronic non-healing wound treatment. In recent years, the therapy with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has become a promising option for chronic wound healing and the efficacy has increasingly been attributed to their exocrine functions. Small extracellular vesicles derived from MSCs (MSC-sEVs) are reported to benefit almost all stages of wound healing by regulating the cellular behavior to participate in the process of inflammatory response, angiogenesis, re-epithelization, and scarless healing. Here, we describe the characteristics of MSC-sEVs and discuss their therapeutic potential in chronic wound treatment. Additionally, we also provide an overview of the application avenues of MSC-sEVs in wound treatment. Finally, we summarize strategies for large-scale production and engineering of MSC-sEVs. This review may possibly provide meaningful guidance for chronic wound treatment with MSC-sEVs.
Keywords: cell dysfunction; chronic non-healing wounds; mesenchymal stem cells; regenerative medicine; small extracellular vesicles.
Copyright © 2023 Wei, Liu, Su, Wang, Chu, Ma, Huang, Li, Fu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Chronic Wound Healing: Current Status of Preclinical and Clinical Studies.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020 Dec;26(6):555-570. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2019.0351. Epub 2020 May 20. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020. PMID: 32242479 Review.
-
Comparison of Curative Effect of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Small Extracellular Vesicles in Treating Osteoarthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Dec 16;16:8185-8202. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S336062. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34938076 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Approach for Kidney Disease Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Aug 13;17:3603-3618. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S372254. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35990308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel neutrophil extracellular trap-related mechanisms in diabetic wounds inspire a promising treatment strategy with hypoxia-challenged small extracellular vesicles.Bioact Mater. 2023 Apr 14;27:257-270. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.04.007. eCollection 2023 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 37122894 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles embedded into methacrylated hyaluronic acid wound dressings accelerate wound repair in a pressure model of diabetic ulcer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Dec 7;21(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02202-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 38062461 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MiR-17-5p-engineered sEVs Encapsulated in GelMA Hydrogel Facilitated Diabetic Wound Healing by Targeting PTEN and p21.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Apr;11(13):e2307761. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307761. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38286650 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Engineered Skin Tissue for Cosmetic Component and Toxicology Detection.Cell Transplant. 2024 Jan-Dec;33:9636897241235464. doi: 10.1177/09636897241235464. Cell Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38491929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress on Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Diabetes and Its Complications.Int J Endocrinol. 2023 Apr 24;2023:9324270. doi: 10.1155/2023/9324270. eCollection 2023. Int J Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37143697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic Profiling of Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exposed to Metal-Based Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 5;26(15):7583. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157583. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806712 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles for chronic wound healing: Bioengineering, standardization, and safety.Regen Ther. 2024 Jun 15;26:260-274. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.06.001. eCollection 2024 Jun. Regen Ther. 2024. PMID: 38978963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

