Circulating exosomal microRNA profiles in migraine patients receiving acupuncture treatment: A placebo-controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 36704329
- PMCID: PMC9871901
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1098766
Circulating exosomal microRNA profiles in migraine patients receiving acupuncture treatment: A placebo-controlled clinical trial
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Circulating exosomal microRNA profiles in migraine patients receiving acupuncture treatment: a placebo-controlled clinical trial.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Apr 20;16:1174810. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1174810. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37152427 Free PMC article.
Abstract
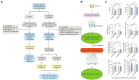
Background: Acupuncture has a long history of being used in Chinese medicine for the treatment of migraine. However, molecular biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of migraine and its treatment are lacking. This study aimed to explore whether acupuncture could regulate differentially expressed exosomal miRNAs between patients with migraine without aura (MWoA) and healthy controls (HCs) and to identify diagnostic biomarkers that helped differentiate MWoA patients from HCs and identify prognostic biomarkers that helped to predict the effect of acupuncture.
Methods: Here, we isolated serum exosomes from patients with MWoA and HCs before and after true and sham acupuncture treatment. Then, small RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis were performed to screen out key miRNAs specifically responding to acupuncture treatment. Pearson's correlation analysis was used to evaluate the correlation between miRNAs and clinical phenotypes. Finally, we applied a machine learning method to identify diagnostic biomarkers of MWoA patients and identify prognostic biomarkers that helped to predict the effect of acupuncture.
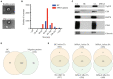
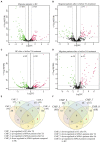
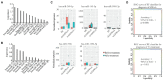
Results: Small RNA sequencing identified 68 upregulated and 104 downregulated miRNAs in MWoA patients compared to those in HCs. Further, we identified eight upregulated and four downregulated miRNAs in migraine patients after true acupuncture treatment (trAMWoA), but not in the sham acupuncture treatment (shAMWoA) or HC group. Among them, has-miR-378a-5p was positively correlated with time unable to work, study, or do housework due to migraine (p < 0.05), whereas has-miR-605-3p was negatively correlated with the restrictive subscale of the migraine-specific quality of life questionnaire (MSQ) (p < 0.05). We then evaluated the diagnostic and prognostic potential of these 12 miRNAs in patients with MWoA. The combination of serum levels of exosomal has-miR-369-5p, has-miR-145-5p, and has-miR-5,010-3p could serve as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for MWoA patients following acupuncture treatment.
Conclusion: This is the first study on the serum exosomal miRNA profiles of migraineurs before and after acupuncture treatment. Our results improve our understanding of the molecular functions of miRNAs in MWoA. More importantly, they expand our view of evaluating the clinical outcomes of migraine patients treated with acupuncture, using exosomal RNA markers.
Clinical trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR2000034417, July 2020.
Keywords: acupuncture; biomarker; exosome; miRNA; migraine.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Qi, Wang, Ni, Gao, Zhou, Chen, He, Sun, Wang, Cai and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum microRNA qPCR profiling and validation indicate upregulation of circulating miR-145-5p and miR-26a-5p in migraineurs.J Headache Pain. 2024 Nov 18;25(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01908-x. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39551757 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of non-invasive biomarkers for chronic atrophic gastritis from serum exosomal microRNAs.BMC Cancer. 2019 Feb 8;19(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5328-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30736753 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture Based on Regulating Autonomic Nerves for the Prevention of Migraine Without Aura: A Prospective, Double-Dummy, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.J Pain Res. 2022 Aug 4;15:2211-2221. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S372311. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35957963 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy prediction of acupuncture treatment for migraine without aura based on multimodal MRI: A study protocol.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 10;13:953921. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.953921. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36299271 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for migraine without aura: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Integr Med. 2018 Sep;16(5):312-321. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 30007828
Cited by
-
MicroRNA profiling in women with migraine: effects of CGRP-targeting treatment.J Headache Pain. 2024 May 16;25(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01787-2. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 38755568 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Proteomic Analysis of Chronic Migraine Exosomes Reveals Disease Patterns and Potential Biomarkers.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):2070-2085. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04389-w. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39066974
-
Serum microRNA qPCR profiling and validation indicate upregulation of circulating miR-145-5p and miR-26a-5p in migraineurs.J Headache Pain. 2024 Nov 18;25(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01908-x. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39551757 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic Analysis from a Descriptive Profile of miRNAs in Chronic Migraine.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 29;25(19):10491. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910491. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408819 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNA in Migraine: A Systemic Literature Review.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;43(7):3315-3327. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01387-9. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37432603 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

