Development and validation of a new robust RP-HPLC method for simultaneous quantitation of insulin and pramlintide in non-invasive and smart glucose-responsive microparticles
- PMID: 36704426
- PMCID: PMC9872181
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.359428
Development and validation of a new robust RP-HPLC method for simultaneous quantitation of insulin and pramlintide in non-invasive and smart glucose-responsive microparticles
Abstract
Background and purpose: Since insulin and pramlintide cooperate in glucose hemostasis, co-administration and quantitation of them in pharmaceutical preparations are imperative. A simple, rapid, sensitive, and isocratic RP-HPLC method was developed and validated for simultaneous quantitation of insulin and pramlintide in loading and in-vitro release studies of a glucose-responsive system to improve the control of hyperglycemic episodes in diabetic patients.
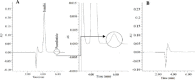
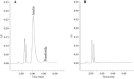
Experimental approach: The isocratic RP-HPLC separation was achieved on a C18 µ-Bondopak column (250 mm × 4.6 mm) using a mobile phase of water:acetonitrile:trifluoroacetic acid (65:35:0.1%) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min in an ambient temperature. Both proteins were detected using a UV detector at 214 nm. The method was validated for specificity, linearity, precision, accuracy, the limit of detection, the limit of quantification, and robustness.
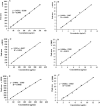
Findings/results: Linearity was obtained in the concentration range of 30 to 360 μg/mL for insulin and 1.5 to 12 μg/mL for pramlintide. The results were validated statistically and recovery studies confirmed the great accuracy and precision of the proposed method. The robustness of the method was also confirmed through small changes in pH, mobile phase composition, and flow rate.
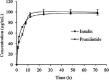
Conclusion and implications: The method was found to be simple, specific, precise, and reproducible. It was applied for the determination of loading capacity, entrapment efficiency, and in-vitro release studies of insulin and pramlintide in a smart glucose-responsive microparticle. Co-delivery of insulin and pramlintide could be a new intervention in diabetes management and concurrent quantitation of these two proteins is, therefore, essential.
Keywords: Diabetes; Insulin; Pramlintide; RP-HPLC; Smart-glucose responsive microparticles.
Copyright: © 2022 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HPLC-UV method development and validation for the quantification of ropinirole in new PLGA multiparticulate systems: Microspheres and nanoparticles.Int J Pharm. 2015 Aug 1;491(1-2):310-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.06.035. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26149934
-
A validated RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of propranolol and valsartan in bulk drug and gel formulation.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2013 Jan;5(1):61-5. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.106573. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2013. PMID: 23559826 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of HPLC method for simultaneous determination of Leflunomide and folic acid in the nanoparticulate system by reversed-phase HPLC.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2023 Aug;49(8):497-507. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2023.2239346. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37470519
-
Method Development and Validation of a Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Quantitative Analysis of Dronedarone Hydrochloride in Pharmaceutical Tablets.Sci Pharm. 2013 Jan-Mar;81(1):115-22. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1209-15. Epub 2012 Nov 5. Sci Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23641332 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid rp HPLC method for quantitative determination of lornoxicam in tablets.J Basic Clin Pharm. 2010 Mar;1(2):115-8. Epub 2010 May 15. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2010. PMID: 24825976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hall JE, Hall ME. Insulin, glucagon, and diabetes mellitus. In: Hall JE, Hall ME, editors. Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology. 14th. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2021. pp. 973–989.
-
- Aronoff SL, Berkowitz K, Shreiner B, Want L. Glucose metabolism and regulation: beyond insulin and glucagon. Diabetes Spectr. 2004;17(3):183–190. doi: 10.2337/diaspect.17.3.183. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
