Microglial autophagy in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 36704504
- PMCID: PMC9872664
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1065183
Microglial autophagy in Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease
Abstract
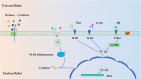
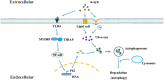
Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) are the most common neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by gradual and selective loss of neurons in the central nervous system. They affect more than 50 million people worldwide, and their incidence increases with age. Although most cases of AD and PD are sporadic, some are caused by genetic mutations that are inherited. Both sporadic and familial cases display complex neuropathology and represent the most perplexing neurological disorders. Because of the undefined pathogenesis and complex clinical manifestations, there is still no effective treatment for both AD and PD. Understanding the pathogenesis of these important neurodegenerative diseases is important for developing successful therapies. Increasing evidence suggests that microglial autophagy is associated with the pathogenesis of AD and PD, and its dysfunction has been implicated in disease progression. In this review, we focus on the autophagy function in microglia and its dysfunction in AD and PD disease models in an attempt to help our understanding of the pathogenesis and identifying new therapeutic targets of AD and PD.
Keywords: AD; PD; autophagy; microglia; neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Wang, Li, Li, Yang and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abiega O., Beccari S., Diaz-Aparicio I., Nadjar A., Layé S., Leyrolle Q., et al. . (2016). Neuronal hyperactivity disturbs ATP microgradients, impairs microglial motility, and reduces phagocytic receptor expression triggering apoptosis/microglial phagocytosis uncoupling. PLoS Biol. 14:e1002466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002466, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S., Kwatra M., Ranjan Panda S., Murty U. S. N., Naidu V. G. M. (2021). Andrographolide suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia through induction of parkin-mediated mitophagy in in-vitro and in-vivo models of Parkinson disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 91, 142–158. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.09.017, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anglade P., Vyas S., Hirsch E. C., Agid Y. (1997). Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson's disease. Histol. Histopathol. 12, 603–610. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

