Effect of bariatric surgery on carotid intima-media thickness: A meta-analysis based on observational studies
- PMID: 36704511
- PMCID: PMC9871789
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1068681
Effect of bariatric surgery on carotid intima-media thickness: A meta-analysis based on observational studies
Abstract
Objective: This meta-analysis aimed to investigate the effect of bariatric surgery on CIMT in people with obesity.
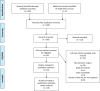
Methods: PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and the Cochrane Library were searched for observational studies assessing the effect of bariatric surgery on CIMT from inception to August 2022. Mean difference (MD) and 95% confidence intervals were calculated to assess CIMT.
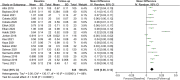
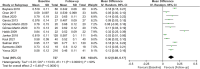
Results: A total of 23 studies, including 1,349 participants, were eligible to participate in this meta-analysis. The results revealed that CIMT was significantly decreased at 6 months, 12 months, and more than 18 months after bariatric surgery compared with baseline (6 months: MD = 0.09; P < 0.01; 12 months: MD = 0.12; P < 0.01; more than 18 months: MD = 0.14; P = 0.02). Meanwhile, laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGB) seemed to be more effective than laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) in lowering CIMT in terms of the type of surgery (LSG: MD = 0.11; P < 0.01; LRYGB: MD = 0.14; P < 0.01). Lastly, the benefits of bariatric surgery on CIMT was independent of gender (Male: MD = 0.06; P = 0.04; Female: MD = 0.08; P = 0.03).
Conclusions: Bariatric surgery is consistently effective in reducing CIMT in people with obesity.
Keywords: bariatric surgery; carotid intima-Media thickness; meta-analysis; obesity; weight loss.
© 2023 Zhou, Jin, Dai, Dai and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
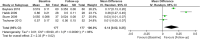


Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis for the effect of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs sleeve gastrectomy in patients with morbid obesity: Evidence from 11 randomized clinical trials (meta-analysis).Int J Surg. 2019 Dec;72:216-223. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.11.013. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Int J Surg. 2019. PMID: 31756544
-
Impact on carotid intima-media thickness after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in patients with morbid obesity.Surg Endosc. 2024 May;38(5):2879-2886. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-10779-x. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Surg Endosc. 2024. PMID: 38519611
-
Comparative analysis of weight loss and resolution of comorbidities between laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 18 studies.Int J Surg. 2020 Apr;76:101-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.035. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 32151750
-
Differences in the effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on gut hormones: systematic and meta-analysis.Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2021 Feb;17(2):444-455. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2020.10.018. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2021. PMID: 33249084
-
A meta-analysis of the medium- and long-term effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.BMC Surg. 2020 Feb 12;20(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12893-020-00695-x. BMC Surg. 2020. PMID: 32050953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, Hong Y, Stern JS, Pi-Sunyer FX, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 American heart association scientific statement on obesity and heart disease from the obesity committee of the council on nutrition, physical activity, and metabolism. Circulation. (2006) 113(6):898–918. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.171016 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

