The clinical significance of serum HMGB1 in patients with lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans after interventional vascular restenosis
- PMID: 36704514
- PMCID: PMC9872960
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1031108
The clinical significance of serum HMGB1 in patients with lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans after interventional vascular restenosis
Abstract
Objective: This study explored the correlation between serum HMGB1 levels and postoperative vascular restenosis in patients with lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans (LEASO).
Methods: A total of 362 patients LEASO who received vascular intervention were recruited in this study. Serum HMGB1 levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify the influencing factors associated with vascular restenosis. The R procedure was used to create nomogram model. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to determine the predictive value of serum HMGB1 and nomogram model for vascular restenosis.
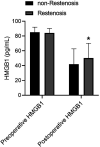
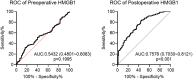
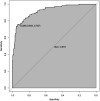
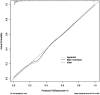
Results: Of the 362 LEASO patients included, 103 (28.45%) developed restenosis within 6 months of postoperative follow-up. Postoperative HMGB1 levels were significantly higher in patients with restenosis compared to those with non-restenosis. Postoperative HMGB1 levels were significantly and positively correlated with the severity of postoperative restenosis (r = 0.819). The AUC of postoperative HMGB1 for the diagnosis of postoperative restenosis was 0.758 (95% CI: 0.703-0.812), with a sensitivity and specificity of 56.31% and 82.24%, respectively. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that diabetes, smoking, regular postoperative medication, increased fibrinogen, decreased red blood cells, increased hs-CRP, and increased postoperative HMGB1 were independently associated with postoperative restenosis in patients with LEASO. The C-index of the nomogram prediction model constructed based on the seven influencing factors mentioned above was 0.918. The nomogram model was significantly more predictive of postoperative restenosis in LEASO patients compared with a single postoperative HMGB1 (AUC: 0.918, 95% CI: 0.757-0.934).
Conclusion: Postoperative serum HMGB1 is an independent risk factor associated with postoperative vascular restenosis in patients with LEASO, and a novel nomogram model based on postoperative serum HMGB1 combined with clinical characteristics may help to accurately predict the risk of postoperative restenosis in patients with LEASO.
Keywords: HMGB1; lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans; nomogram model; vascular interventional therapy; vascular restenosis.
© 2023 Yang and XiaPing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship Between Serum HMGB1 and RAGE Levels and Restenosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Complicated With Lower Extremity Vascular Disease: A Retrospective Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Feb 2;18:315-325. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S496360. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 39925465 Free PMC article.
-
Increased plasma olfactomedin 2 after interventional therapy is a predictor for restenosis in lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans patients.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2018 Jul;78(4):269-274. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2018.1452287. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2018. PMID: 29553861
-
Expression level and clinical significance of LncRNA PVT1 in the serum of patients with LEASO.PeerJ. 2023 Sep 19;11:e16057. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16057. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37744231 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlation between C-reactive protein to albumin ratio and restenosis after femoral popliteal stenting in patients with lower extremity arteriosclerotic obliterans].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Dec 1;61(12):1058-1064. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20230815-00047. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37932141 Chinese.
-
Effect of diabetes on the prognosis, serum inflammatory factors, and quality of life of patients with lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans after vascular intervention: a retrospective comparative cohort study.Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Aug;11(8):2720-2729. doi: 10.21037/apm-22-827. Ann Palliat Med. 2022. PMID: 36064362
Cited by
-
Relationship Between Serum HMGB1 and RAGE Levels and Restenosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Complicated With Lower Extremity Vascular Disease: A Retrospective Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Feb 2;18:315-325. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S496360. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 39925465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conte MS, Pomposelli FB, Clair DG, Geraghty PJ, McKinsey JF, Mills JL, et al. Society for vascular surgery practice guidelines for atherosclerotic occlusive disease of the lower extremities: management of asymptomatic disease and claudication. J Vasc Surg. (2015) 61:2s–41s. 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.12.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liistro F, Porto I, Angioli P, Grotti S, Ricci L, Ducci K, et al. Drug-eluting balloon in peripheral intervention for below the knee angioplasty evaluation (DEBATE-BTK): a randomized trial in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia. Circulation. (2013) 128:615–21. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001811 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

