Association between epidural-related maternal fever and short-and long-term prognosis of parturients: A prospective observational study
- PMID: 36704517
- PMCID: PMC9871620
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1064272
Association between epidural-related maternal fever and short-and long-term prognosis of parturients: A prospective observational study
Abstract
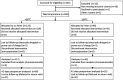
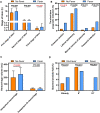
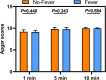
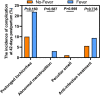
We aimed to explore the association between epidural-related maternal fever (ERMF) and prognosis of parturients. 159 parturients who underwent vaginal delivery under labor epidural analgesia (LEA) received noninvasive continuous core body temperature monitoring. 122 of them completed the 42-day postpartum follow-up. Parturients with body temperature ≥38°C during labor were categorized as the Fever group, while the others were categorized as the No-Fever group. Compared to No-Fever group, Fever group had a greater proportion of primiparas, greater gestational age of parturients, and longer third stage of labor. The cesarean section and forceps delivery rates, and the amount of intrapartum hemorrhage in Fever group were significantly higher. There were no significant between-group differences with respect to puerperal infection, and amniotic fluid turbidity degree, neither significant between-group difference at 42-days postpartum. We found that ERMF was associated with some short-term outcomes. However, it showed no relation with long-term prognosis of the parturients at 42-days postpartum.
Keywords: epidural-related; fever; labor epidural analgesia; long-term; maternal.
© 2023 Li, Liao, Wang, He, Yang, Jia and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and epidural-related maternal fever in Chinese parturients: a prospective cohort study.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2024 Dec;37(1):2376657. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2024.2376657. Epub 2024 Jul 8. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2024. PMID: 38977394
-
The relationship between epidural analgesia and intrapartum maternal fever and the consequences for maternal and neonatal outcomes: a prospective observational study.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Dec;35(25):5354-5362. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2021.1879042. Epub 2021 Jan 27. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022. PMID: 33504250
-
[Effect of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation on epidural-related maternal fever in parturients undergoing epidural labor analgesia].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Jul 25;46(7):586-91. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200616. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34369679 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Concerned topics of epidural labor analgesia: labor elongation and maternal pyrexia: a systematic review.Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Mar 5;133(5):597-605. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000646. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020. PMID: 32032081 Free PMC article.
-
Epidural analgesia during labor.Am Fam Physician. 1998 Nov 15;58(8):1785-92. Am Fam Physician. 1998. PMID: 9835854 Review.
Cited by
-
Low lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio and accelerated temperature rise in epidural-related maternal fever: a prospective cohort study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Jun 3;25(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03157-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40461993 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of early- and late- neuraxial analgesia on multiparous women: a retrospective monocentric study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02395-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38166749 Free PMC article.
-
Fever in childbirth: a mini-review of epidural-related maternal fever.Front Neurosci. 2024 Apr 19;18:1389132. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1389132. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38707593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influencing factors of intrapartum fever after epidural labor analgesia.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024 Oct 25;70(11):e20240565. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20240565. eCollection 2024. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2024. PMID: 39475917 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

