Effects of milk replacer feeding level on growth performance, rumen development and the ruminal bacterial community in lambs
- PMID: 36704552
- PMCID: PMC9871810
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1069964
Effects of milk replacer feeding level on growth performance, rumen development and the ruminal bacterial community in lambs
Abstract
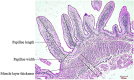
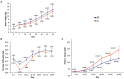
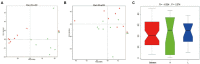
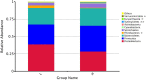
Feeding with a suitable level of milk replacer (MR) can improve the survival rate and stimulate the growth potential of early lambs. However, feeding excessive MR might be detrimental to rumen development and microbial colonization. Herein, we investigated the effects of feeding different levels of MR on rumen digestive function and ruminal microorganisms. Fourteen healthy male Hu lambs with similar birth weights and detailed pedigree records were divided into two groups to receive low (2% of average body weight per day) and high (4% of average body weight per day) levels of MR. We analyzed the effects of the MR feeding level on growth performance, fiber degradation rates, rumen fermentation parameters, enzyme activities and rumen histomorphology. We found that feeding with a high level of MR improved the average daily gain of early lambs, but decreased the starter intake, rumen weight and papillae length. We also analyzed the effects of the MR feeding level on the rumen microbiota using 16S-rRNA amplicon sequencing data. The results showed that high a MR feeding level increased the rumen microbial diversity but decreased the abundance of many carbohydrate degrading bacteria. Several bacterial genera with significant differences correlated positively with rumen cellulase activity and the acid detergent fiber degradation rate. Our results suggested that a high level of MR could improve the growth performance of early lambs in the short term; however, in the long term, it would be detrimental to rumen development and have adverse effects on the adaptation process of the microbiota to solid feed.
Keywords: fiber degradation; lambs; milk replacer; rumen development; rumen fermentation; rumen microbiota.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Wang, Zhang, Chen, Li, Wang, Zhang, Wang, Zhang, Cui and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alfalfa Intervention Alters Rumen Microbial Community Development in Hu Lambs During Early Life.Front Microbiol. 2018 Mar 27;9:574. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00574. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29636743 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of supplementary feeding on the rumen morphology and bacterial diversity in lambs.PeerJ. 2020 Jun 19;8:e9353. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9353. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32596052 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of milk replacer feeding strategies on performance, ruminal development, and metabolism of dairy calves.J Dairy Sci. 2014 Feb;97(2):1016-25. doi: 10.3168/jds.2013-7201. Epub 2013 Dec 15. J Dairy Sci. 2014. PMID: 24342682 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of physical forms of starter feed on growth, nutrient digestibility, gastrointestinal enzyme activity, and morphology of pre- and post-weaning lambs.Animal. 2021 Jan;15(1):100044. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2020.100044. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Animal. 2021. PMID: 33516036
-
Early Feeding Regime of Waste Milk, Milk, and Milk Replacer for Calves Has Different Effects on Rumen Fermentation and the Bacterial Community.Animals (Basel). 2019 Jul 15;9(7):443. doi: 10.3390/ani9070443. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31311119 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The characteristics, influence factors, and regulatory strategies of growth retardation in ruminants: a review.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 26;12:1566427. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1566427. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40206254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Holstein steers growth performance: oregano essential oil's impact on rumen development, functionality and microorganism.Anim Microbiome. 2025 May 6;7(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s42523-025-00415-x. Anim Microbiome. 2025. PMID: 40329403 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Rumen Microbiota and Serum Metabolite Profile of Hainan Black Goats with Different Body Weights before Weaning.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 28;14(3):425. doi: 10.3390/ani14030425. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38338068 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis to Elucidate the Effects of Milk Replacer Feeding Level on Intestinal Function and Development of Early Lambs.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 24;13(11):1733. doi: 10.3390/ani13111733. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37889672 Free PMC article.
-
Oregano essential oil enhanced body weight and well-being by modulating the HPA axis and 23-nordeoxycholic acid of cecal microbiota in Holstein steers under cold stress.Anim Microbiome. 2025 Apr 1;7(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s42523-025-00401-3. Anim Microbiome. 2025. PMID: 40170088 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

