A unified and simple medium for growing model methanogens
- PMID: 36704566
- PMCID: PMC9871610
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1046260
A unified and simple medium for growing model methanogens
Abstract
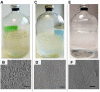
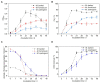
Apart from their archetypic use in anaerobic digestion (AD) methanogenic archaea are targeted for a wide range of applications. Using different methanogenic archaea for one specific application requires the optimization of culture media to enable the growth of different strains under identical environmental conditions, e.g., in microbial electrochemical technologies (MET) for (bio)electromethanation. Here we present a new culture medium (BFS01) adapted from the DSM-120 medium by omitting resazurin, yeast extract, casitone, and using a low salt concentration, that was optimized for Methanosarcina barkeri, Methanobacterium formicicum, and Methanothrix soehngenii. The aim was to provide a medium for follow-up co-culture studies using specific methanogens and Geobacter spp. dominated biofilm anodes. All three methanogens showed growth and activity in the BFS01 medium. This was demonstrated by estimating the specific growth rates ( ) and doubling times ( ) of each methanogen. The and based on methane accumulation in the headspace showed values consistent with literature values for M. barkeri and M. soehngenii. However, and based on methane accumulation in the headspace differed from literature data for M. formicicum but still allowed sufficient growth. The lowered salt concentration and the omission of chemically complex organic components in the medium may have led to the observed deviation from and for M. formicicum as well as the changed morphology. 16S rRNA gene-based amplicon sequencing and whole genome nanopore sequencing further confirmed purity and species identity.
Keywords: bioelectrochemical systems; doubling time; medium adaptation; methanogenic archaea; microbial electrochemical technology; specific growth rate.
Copyright © 2023 Dzofou Ngoumelah, Harnisch, Sulheim, Heggeset, Aune, Wentzel and Kretzschmar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of model methanogens on the electrochemical activity, stability, and microbial community structure of Geobacter spp. dominated biofilm anodes.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Mar 5;10(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00490-z. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 38443373 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Evidence for Isopotential Tunneling in the Electron Transport Chain of Methane-Producing Archaea.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Aug 31;83(18):e00950-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00950-17. Print 2017 Sep 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28710268 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Geobacter spp. Dominated Biofilms and Anaerobic Digestion Effluents─The Effect of Effluent Composition and Electrode Potential on Biofilm Activity and Stability.Environ Sci Technol. 2023 Feb 14;57(6):2584-2594. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c07574. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Environ Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 36731122
-
Putative Extracellular Electron Transfer in Methanogenic Archaea.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 22;12:611739. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.611739. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33828536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor--a review.Indian J Environ Health. 2001 Apr;43(2):1-82. Indian J Environ Health. 2001. PMID: 12397675 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the low-rank coal degradation efficiency bioaugmented with activated sludge.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 27;14(1):14827. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64275-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38937498 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of model methanogens on the electrochemical activity, stability, and microbial community structure of Geobacter spp. dominated biofilm anodes.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Mar 5;10(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00490-z. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 38443373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bryant M. P., Boone D. R. (1987a). Emended description of strain MST (DSM 800T), the type strain of Methanosarcina barkeri. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 169–170. doi: 10.1099/00207713-37-2-169 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

