Clinical Profile, Histopathology, and Outcomes in Infection-Related Glomerulonephritis - Single-Center Experience
- PMID: 36704600
- PMCID: PMC9872921
- DOI: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_470_20
Clinical Profile, Histopathology, and Outcomes in Infection-Related Glomerulonephritis - Single-Center Experience
Abstract
Background: Infection-related glomerulonephritis (IRGN) is an important source of renal morbidity with adverse outcomes in adults. Data from large centers in India is lacking on this common, yet poorly understood entity.
Materials and methods: We performed a prospective observational study of all patients diagnosed with IRGN at our center over a 3-year period between 2017 and 2019. "Typical IRGN" patients were diagnosed based on clinical and laboratory assessment; others underwent renal biopsy. Renal and patient survival outcomes were assessed in addition to factors that help predict outcomes.
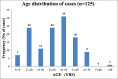
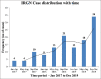
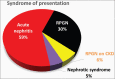
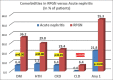
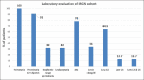
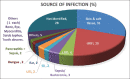
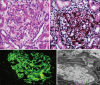
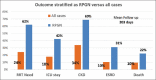
Results: One hundred and twenty-five patients with a diagnosis of IRGN were included in the study, including 86 patients who underwent renal biopsy. This represented 24% of all biopsies during this time period, and IRGN was the most common nondiabetic kidney disease identified in diabetic biopsies at our center. Female preponderance and a seasonal variation were striking. Atypical sources of infection like otomycosis, tooth abscess, and dengue virus infection were noted. Male gender and diabetes were important risk factors for severe disease. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN), atypical serum complement profiles, and comorbid illnesses were common in adults. Though children had more benign disease and outcomes, life-threatening complications were also noted. C3 dominance was the most striking immunofluorescence (IF) finding and was associated with poorer outcomes. Crescentic IRGN was rare, and four cases of IgA-dominant IRGN were noted. Also, 24% of the cohort required renal replacement therapy. RPGN presentation of IRGN portended worst prognosis with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in 31% and death in 22% of patients.
Conclusion: IRGN is a common clinical entity in adults with the potential for adverse renal and survival outcomes. We have identified clinical and biopsy characteristics that are associated with ESRD and death.
Keywords: IgA-Dominant IRGN; infection-related glomerulonephritis; outcomes; renal biopsy.
Copyright: © 2022 Indian Journal of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IgA-dominant Infection-related Glomerulonephritis in India: A Single-center Experience.Indian J Nephrol. 2017 Nov-Dec;27(6):435-439. doi: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_337_16. Indian J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 29217879 Free PMC article.
-
The features in IgA-dominant infection-related glomerulonephritis distinct from IgA nephropathy: a single-center study.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018 Oct;22(5):1116-1127. doi: 10.1007/s10157-018-1564-4. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29564665
-
The Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Outcome of Infection-related Glomerulonephritis from East India: A Single Center Experience.Indian J Nephrol. 2017 Jul-Aug;27(4):307-312. doi: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_280_16. Indian J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28761234 Free PMC article.
-
Clinico-Pathogenic Similarities and Differences between Infection-Related Glomerulonephritis and C3 Glomerulopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 8;24(9):8432. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098432. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial infection-related glomerulonephritis in adults.Kidney Int. 2013 May;83(5):792-803. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.407. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23302723 Review.
References
-
- Nasr SH, Radhakrishnan J, D’Agati VD. Bacterial infection-related glomerulonephritis in adults. Kidney Int. 2013;83:792–803. - PubMed
-
- Natarajan G, Ramanathan S, Jeyachandran D, Balasubramaniyan T, Srinivasa Prasad ND, Thanigachalam D. Follow-up study of post-infectious glomerulonephritis in adults: Analysis of predictors of poor renal outcome. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant. 2014;25:1210–6. - PubMed
-
- Montseny JJ, Meyrier A, Kleinknecht D, Callard P. The current spectrum of infectious glomerulonephritis. Experience with 76 patients and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1995;74:63–73. - PubMed
-
- Kumar R, Vohra H, Chakraborty A, Sharma YP, Bandhopadhya S, Dhanda V, et al. Epidemiology of group A streptococcal pharyngitis & impetigo: A cross-sectional & follow up study in a rural community of northern India. Indian J Med Res. 2009;130:765–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
