A novel class of C14-sulfonate-tetrandrine derivatives as potential chemotherapeutic agents for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36704617
- PMCID: PMC9871304
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1107824
A novel class of C14-sulfonate-tetrandrine derivatives as potential chemotherapeutic agents for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
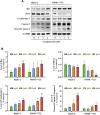
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common malignancy of the liver, exhibits high recurrence and metastasis. Structural modifications of natural products are crucial resources of antitumor drugs. This study aimed to synthesize C-14 derivatives of tetrandrine and evaluate their effects on HCC. Forty C-14 sulfonate tetrandrine derivatives were synthesized and their in vitro antiproliferative was evaluated against four hepatoma (HepG-2, SMMC-7721, QGY-7701, and SK-Hep-1) cell lines. For all tested cells, most of the modified compounds were more active than the lead compound, tetrandrine. In particular, 14-O-(5-chlorothiophene-2-sulfonyl)-tetrandrine (33) exhibited the strongest antiproliferative effect, with half-maximal inhibitory concentration values of 1.65, 2.89, 1.77, and 2.41 μM for the four hepatoma cell lines, respectively. Moreover, 33 was found to induce apoptosis via a mitochondria-mediated intrinsic pathway via flow cytometry and western blotting analysis. In addition, colony formation, wound healing, and transwell assays demonstrated that 33 significantly inhibited HepG-2 and SMMC-7721 cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, indicating that it might potentially be a candidate for an anti-HCC therapy in the future.
Keywords: anti-HCC; anti-migration; apoptosis; sulfonate derivatives; tetrandrine derivatives.
Copyright © 2023 Jiang, Xie, Zeng, Lan, Liu, Li, Ren, Chen and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

